What is Amazon ElastiCache?
Amazon ElastiCache is a Caching-as-a-Service of Amazon Web Services. AWS simplifies setting up, managing, and scaling a distributed in-memory cache environment in the cloud platform. It provides a high-performance, scalable, & cost-effective caching solution. AWS removes the complexity associated with deploying & managing a distributed cache environment.
Caching is a technique to store frequently accessed information, HTML pages, images, videos and other static information in a temporary memory location on the server. Read-intensive web applications are the best use-case candidates for a cache service available in the AWS.
Introduction
In a web-driven world, catering to users’ requests in real-time is the goal of every website. Because performance & speed are required, a caching layer, like Amazon ElastiCache, is the first tool that every website employs in serving mostly static and frequently accessed data.
Why ElastiCache?
There are a number of caching servers used across applications, the most notable are memcached, Redis, and Varnish. There are various methods to implement caching using those technologies. However, with such a large number of industries moving their infrastructure to the cloud, many cloud vendors are also providing caching as a service.
Amazon ElastiCache is one of the popular web caching service which provides users with memcached or Redis-based caching that supports installation, configuration, HA, Caching failover and clustering.
How Amazon ElastiCache Works?
There are two engine software contains in Amazon ElastiCache wich explore given below:
memcached
memcached is an open-source, distributed, in-memory key-value store-caching system for small arbitrary data streams flowing from database calls, API calls, or page rendering. memcached has long been the first choice of caching technology for users and developers around the world.
Redis
Redis is a newer technology and often considered as a superset of memcached. That means Redis offers more and performs better than memcached. Redis scores over memcached in a few areas that we will discuss briefly.
- Redis implements six fine-grained policies for purging old data, while memcached uses the LRU (Least Recently Used) algorithm.
- Redis supports key names and values up to 512 MB, whereas memcached supports only 1 MB.
- Redis uses a hashmap to store objects whereas memcached uses serialized strings.
- Redis provides a persistence layer and supports complex types like hashes, lists (ordered collections, meant for queue), sets (unordered collections of non-repeating values), or sorted sets (ordered/ranked collections of non-repeating values).
- Redis is used for built-in pub/sub, transactions (with optimistic locking), and Lua scripting.
- Redis 3.0 supports clustering.
Amazon Elasticache Features
The Amazon ElastiCache has features to enhance reliability for critical production deployments, including:
- Automatic detection & recovery from cache node failures.
- Automatic failover (Multi-AZ’s) of a failed primary cluster to a read replica in Redis replication groups.
- Flexible Availability Zone placement of nodes and clusters to avoid downtime.
- Integration with other Amazon Web Services such as Amazon EC2, CloudWatch, CloudTrail, and Amazon SNS, to provide a secure, high-performance, managed in-memory caching solution.
Amazon ElastiCache provides two caching engine software, memcached and Redis. You can move your existing memcached or Redis caching implementation to an Amazon ElastiCache effortlessly. Simply change the memcached/Redis endpoints in your application.
Before implementing Amazon ElastiCache, let’s get familiar with a few related Keypoints:
ElastiCache Node
Nodes are the smallest building block of Amazon ElastiCache service, which are typically network-attached RAMs (each having an independent DNS name & port).
ElastiCache Cluster
Clusters are logical collections of nodes. If your ElastiCache cluster is of memcached nodes, you can have nodes in multiple availability zones (AZs) to implement high-availability. In a case of a Redis cluster, the cluster is always a single node. You can have multiple replication groups across AZs.
A memcached cluster has multiple nodes whose cached data is horizontally partitioned among each node. Each of the nodes in the cluster is capable of reading and writing.
A Redis cluster has only one node, which is the master node. Redis clusters do not support data partitioning. Rather, there are up to five replication nodes in-replication groups which are read-only. They maintain copies from the master node which is the only writeable node.
ElastiCache memcached
Until now we have discussed both the caching engines, but I may seem biased towards Redis. So the question is, if Redis is all enough, then why doesn’t ElastiCache provide only Redis? There are a few good reasons for using memcached:
- It is the simplest caching model.
- It is helpful for people needing to run large nodes with multiple cores or threads.
- It offers the ability to scale out/in, adding & removing nodes on-demand.
- It handles partitioning data across multiple shards.
- It handles cache objects, such as a database.
- It may be necessary to support an existing memcached cluster.
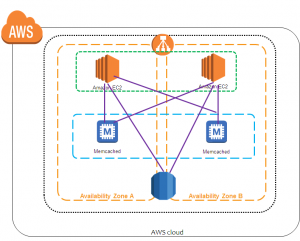
memcached cluster
Each node in the memcached cluster has its own endpoint. The cluster in memcached also has an endpoint called the configuration endpoint. If you enable Auto-Discovery and connect to the configuration endpoint, your application will automatically know each node endpoint – even after adding or removing nodes from the cluster. The latest version of memcached supported in Amazon ElastiCache is 1.4.24.
In the memcached-based ElastiCache cluster, there can be a maximum of 20 nodes where data is horizontally partitioned. If you require more, you’ll have to request a limit increase via the ElastiCache Limit Increase Request form.
Apart from that, you can upgrade the memcached engine. Keep in mind that the memcached engine upgrade process is disruptive. The cached data is lost in any existing cluster when you upgrade.
Changing the number of nodes in a cluster is only possible for a memcached-based ElastiCache cluster. However, this operation requires careful design of the hashing technique you will use to map the keys across the nodes. One of the best techniques is to use a consistent hashing algorithm for keys.
Consistent hashing uses an algorithm such that whenever a node is added or removed from a cluster, the number of keys that must be moved is roughly 1 / n (where n is the new number of nodes).
1)Scaling from 1 to 2 nodes results in 1/2 (50 %) of the keys being move — the worst case.
2)Scaling from 9 to 10 nodes results in 1/10 (10 percent) of the keys being move. An unsuitable algorithm will result in heavy cache misses, thus increasing the load on a database & defeating the purpose of a caching layer.
ElastiCache Redis
We have discussed Redis & the replication groups earlier. All things considered, Redis will normally be the better selection:
- Redis supports complex data types, such as strings, hashes, lists, & sets.
- Redis sorts or ranks in-memory data-sets.
- Redis provides persistence for your key store.
- Redis replicates the cache data from the primary to one or more read replicas for read intensive applications.
- Redis has automatic fail-over capabilities if the primary node fails.
- Redis has publish & subscribe (pub/sub) capabilities where the client is inform of events on the server.
- Redis has back-up and restore capabilities.
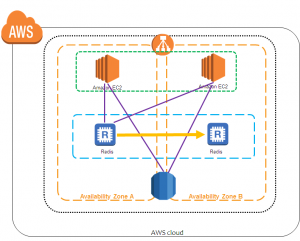
Currently, Amazon ElastiCache supports Redis 2.8.23 and lower. Redis-2.8.6 and higher is a significant step up because a Redis cluster on version 2.8.6 or higher will have Multi-AZ enabled. Upgrading is a non-disruptive process and the cache data is retain.
If you want to persist the cache data, Redis has something called Redis AOF (Append Only File). AOF file is useful in recovery scenarios. In the case of a node restart /service crash, Redis will replay the updates from an AOF file, thereby recovering the data lost. But AOF is not useful in the event of a hardware crash and AOF operations are slow.
AOF operations
A better way is to have a replication group with one or more read replicas in different availability zones & enable Multi-AZ instead of using AOF. Because there is no need for AOF in this scenario, ElastiCache disables AOF on Multi-AZ replication groups.
All the nodes in a replication group reside in the same region but in multiple availability zones (AZs). An ElastiCache replication group consists of a primary cluster & up to five read replicas. In the case of a primary cluster or availability zone failure, if your replication group is Multi-AZ enabled, ElastiCache will automatically detect the primary cluster’s failure, select a read replica cluster, & promote it to primary cluster so that you can resume writing to the new primary cluster as soon as the promotion is complete.
ElastiCache also propagates the DNS of the promoted replica so that, if your application is writing to the primary endpoint, no endpoint change will be required in your application. Make sure that your cache engine is Redis-2.8.6 or higher and have instance types higher than t1 and t2 nodes.
Redis cluster supports backup and restores processes. It is useful when you want to create a new cluster from existing cluster data.
Conclusion
Amazon ElastiCache offloads the management, monitoring, & operation of caching clusters in the cloud. It has detailed monitoring via Amazon CloudWatch without any extra cost overhead and is a pay-as-you-go service. I encourage you to use ElasticCache for your cloud-based web applications requiring split-second response times.
#Last but not least, always ask for help!



