Hadoop Basic Linux Commands
Hadoop Basic Linux Commands
Welcome to the world of best Linux commands used in Hadoop, In This tutorial, one can easily learn a List of all Top Rated Hadoop basic Linux commands which are available and are used by most of the Hadoop developers. Are you also dreaming to become to certified Pro Developer, then stop just dreaming get your Hadoop certification course from India’s Leading Big Data Training institute.
So follow the below mentioned basic Linux commands for Hadoop from Prwatech and learn Hadoop Course like a pro from today itself under 15+ Years of Hands-on Experienced Professionals.

Basic Linux commands used in Hadoop
ls ⇒ directory listing

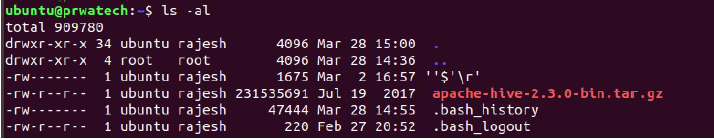
ls -al ⇒ formatted listing with hidden files
cd dir ⇒ change directory to dir

cd ⇒ change to home

pwd ⇒ shows current directory

mkdir dir ⇒ create a directory dir

rm file ⇒ delete the file
![]()
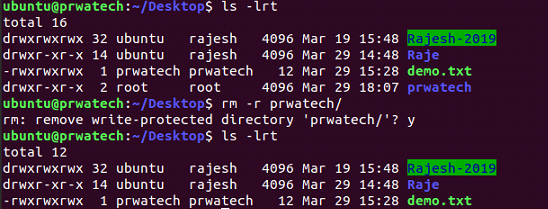
rm -r dir ⇒ delete directory dir
rm -f file ⇒ force remove the file
![]()
rm -rf dir ⇒ force remove directory dir *
![]()
cp file1 file2 ⇒ Copy file1 to file2
![]()
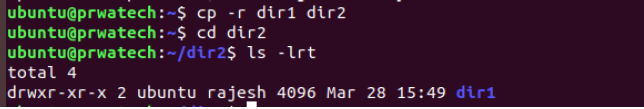
cp -r dir1 dir2 ⇒ copy dir1 to dir2; create dir2 if it is not present.
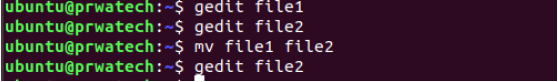
mv file1 file2 ⇒ rename or move file1 to file2 if file2 is an existing directory, moves file1 into
directory file2
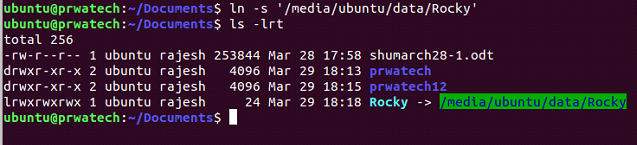
ln -s file link ⇒ create a symbolic link to file
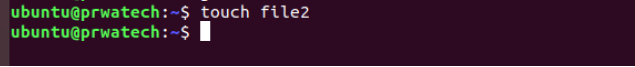
touch file ⇒ create or update file
cat > file ⇒ places standard input into the file

more file ⇒ output the contents of the file

head file ⇒ output the first 10 lines of the file

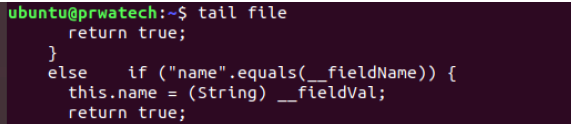
tail file ⇒ output the last 10 lines of the file
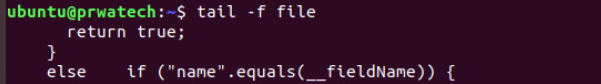
tail -f file ⇒ output the contents of the file as it
grows, starting with the last 10 lines
Permission Commands:
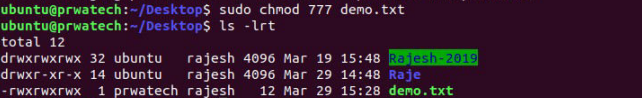
chmod ⇒ modify file access rights
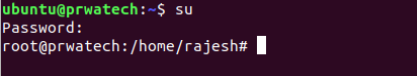
su ⇒ temporarily become the superuser
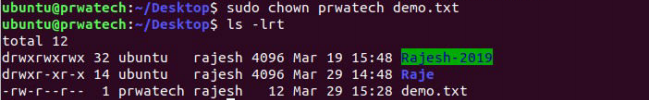
sudo ⇒ temporarily become the superuser

chowm ⇒ change file ownership
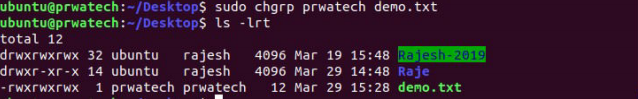
chgrp ⇒ change a file’s group ownership
System Info Commands :
date ⇒ shows the current date and time

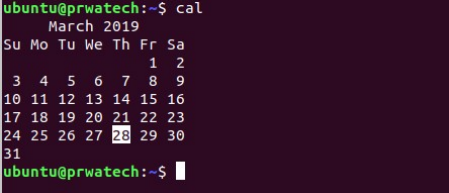
cal ⇒ show this month’s calendar
uptime ⇒ show current uptime

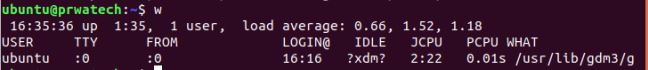
w ⇒ display who is online
whoami ⇒ who you are logged in as

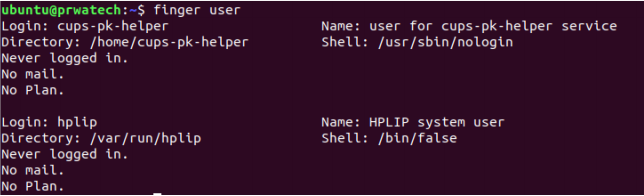
finger user ⇒ display information about user
uname -a ⇒ show kernel information

cat /proc/cpuinfo ⇒ cpu information
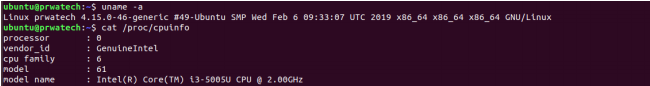
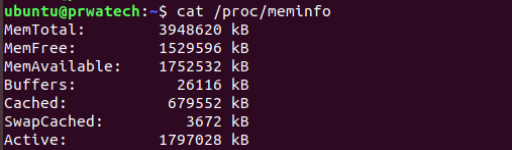
cat /proc/meminfo ⇒ memory information
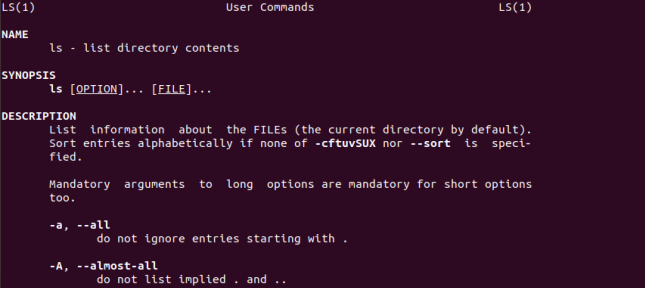
man command ⇒ show the manual for command
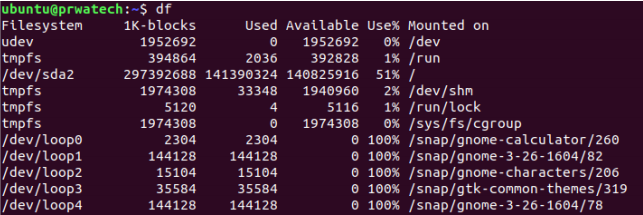
df ⇒ show disk usage
du ⇒ show directory space usage
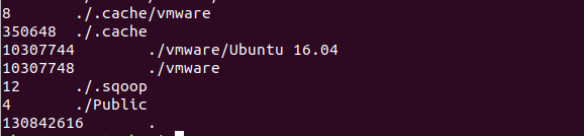
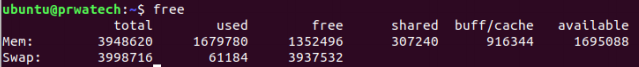
free ⇒ show memory and swap usage
whereis app ⇒ show possible locations of app
![]()
which app ⇒ show which app will be run by default

Process Management Commands:
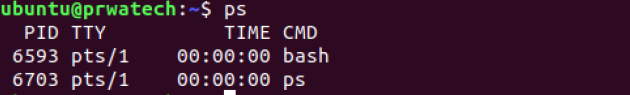
ps ⇒ display your currently active processes
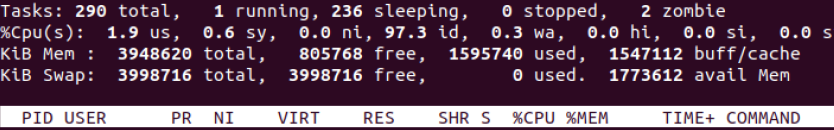
top ⇒ display all running processes
kill pid ⇒ kill process id pid
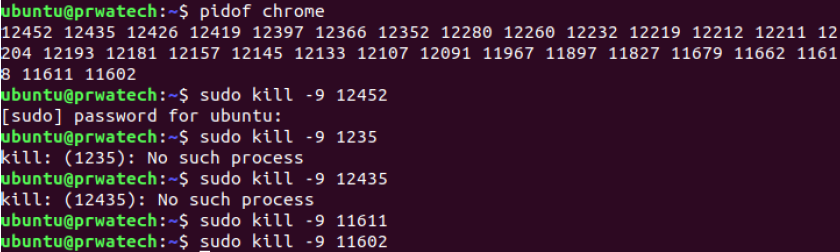
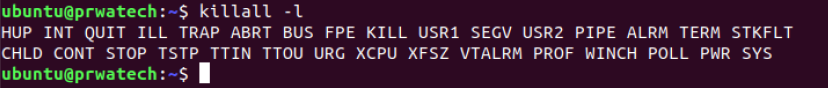
killall proc ⇒ kill all processes named proc *
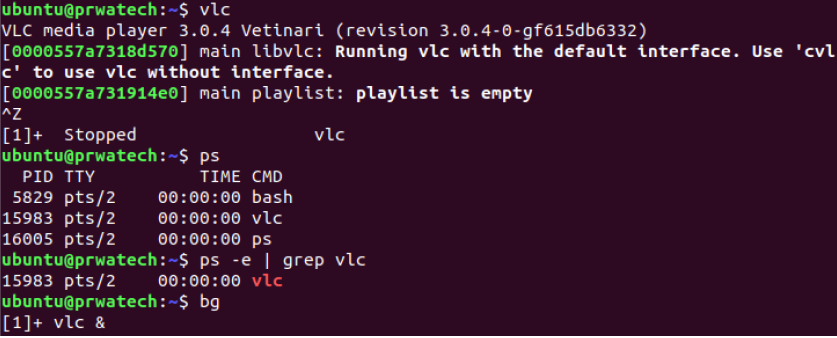
bg ⇒ lists stopped or background jobs; resume a
stopped job in the background
fg ⇒ brings the most recent job to foreground
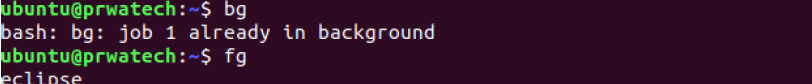
fg n ⇒ brings job n to the foreground
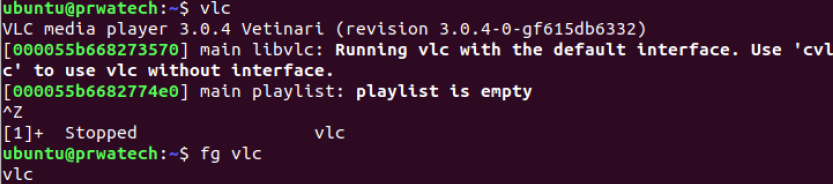
SSH Commands
sshuser@host ⇒ connect to host as the user
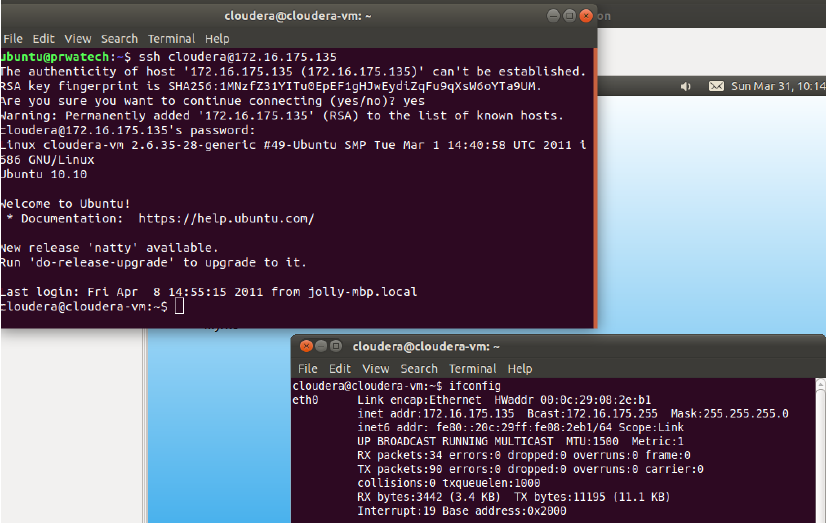
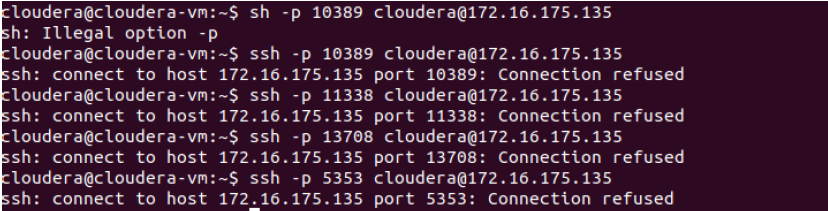
ssh -p port user@host ⇒ connect to host on port
port as user
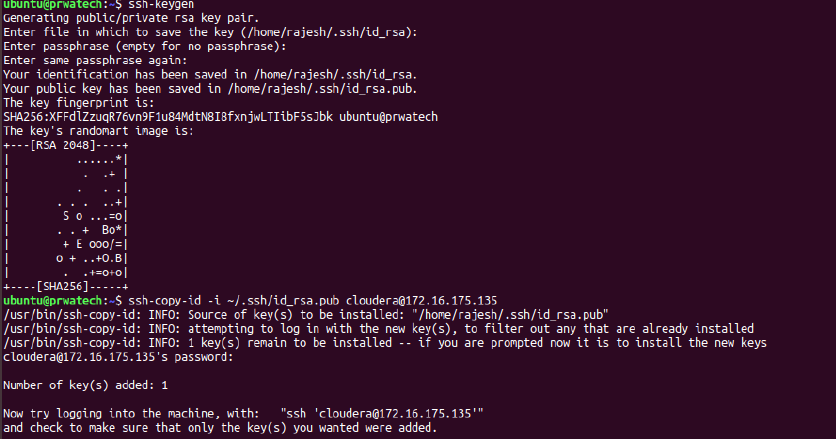
ssh-copy-id user@host ⇒ add your key to host for
user to enable a keyed or passwordlesslogin
Searching Commands
grep pattern files ⇒ search for pattern in files
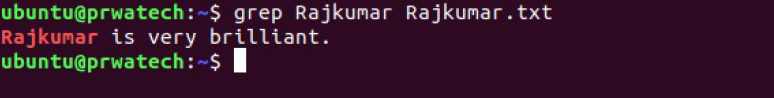
grep -r pattern dir ⇒ search recursively for
pattern in dir
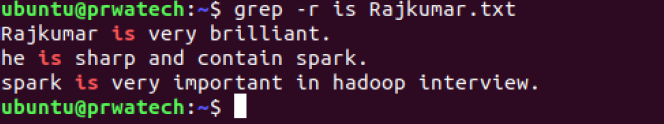
command | grep pattern ⇒ search for pattern in the output of the command
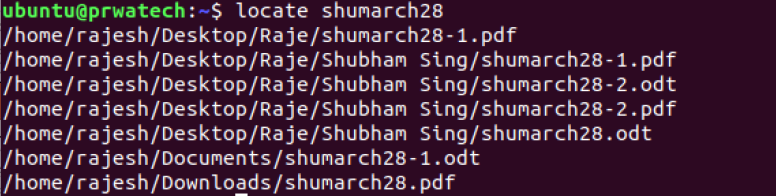
locate file ⇒ find all instances of file
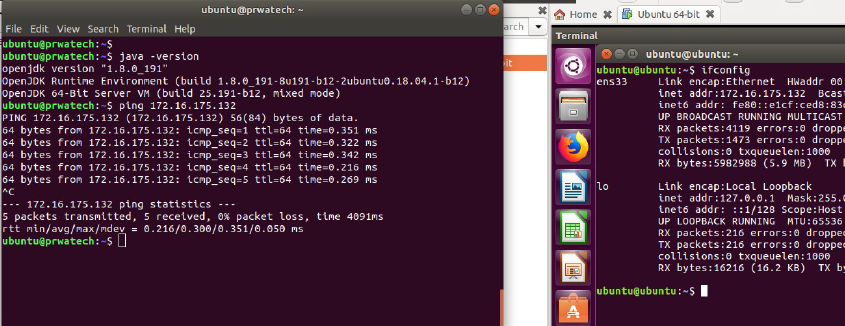
Network Commands
ping host ⇒ ping host and output results
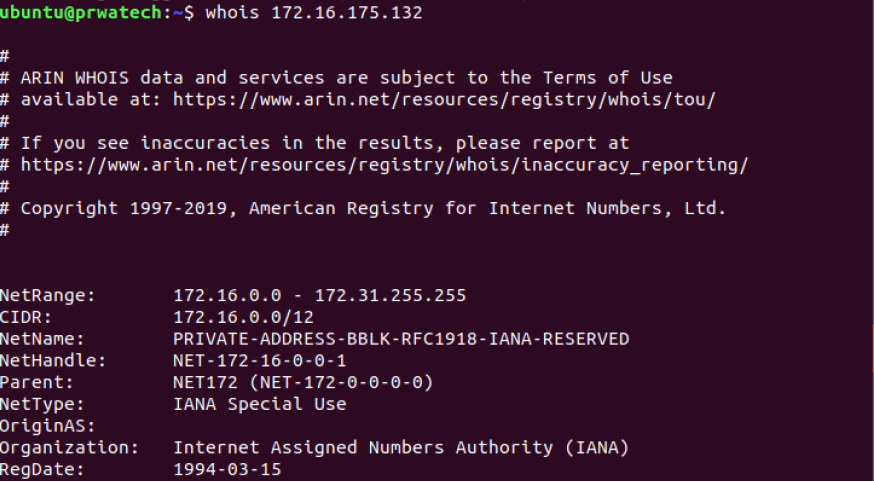
whois domain ⇒ get whoisinformation for domain
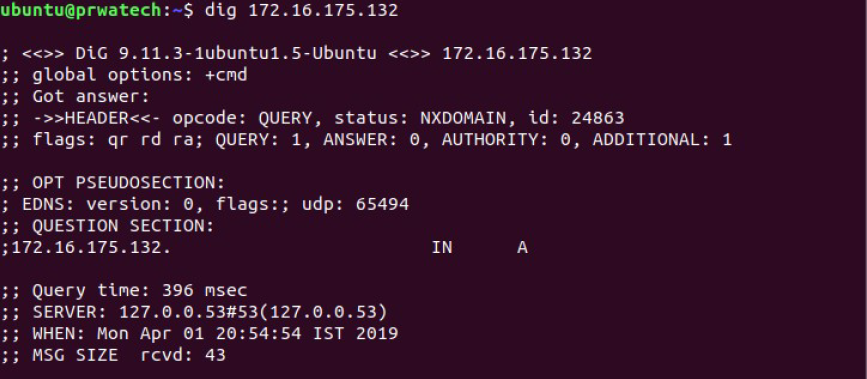
dig domain ⇒ get DNS information for domain
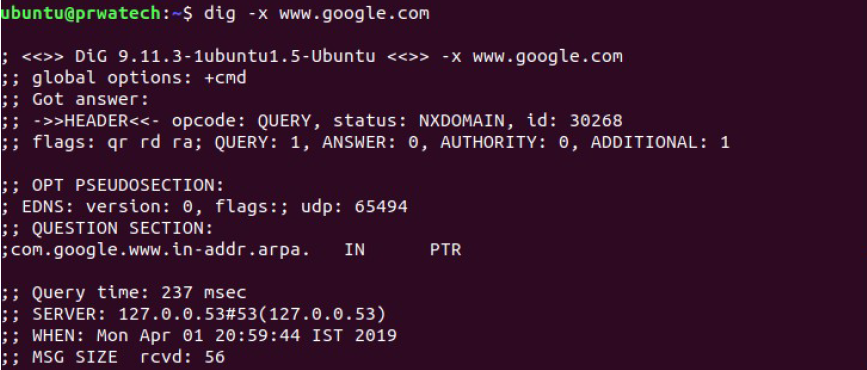
dig -x host ⇒ reverse lookup host
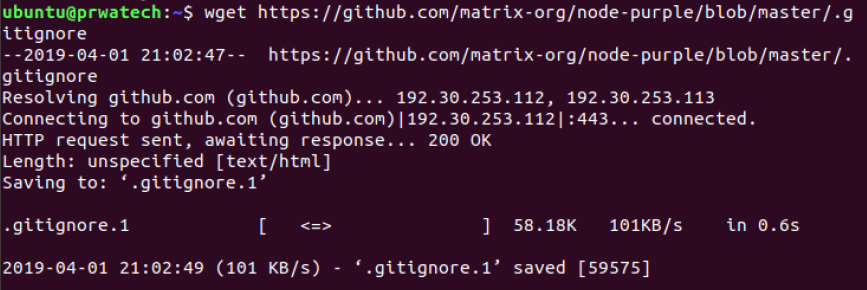
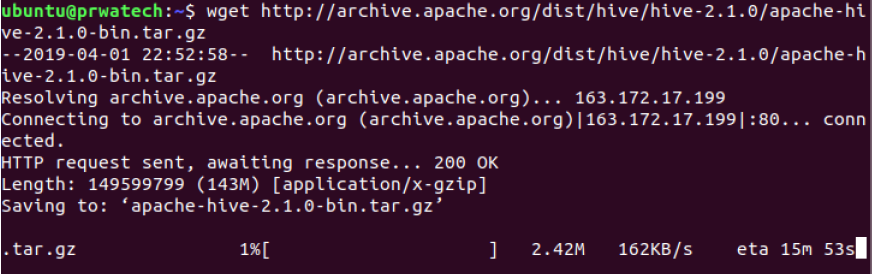
wget file ⇒ download file
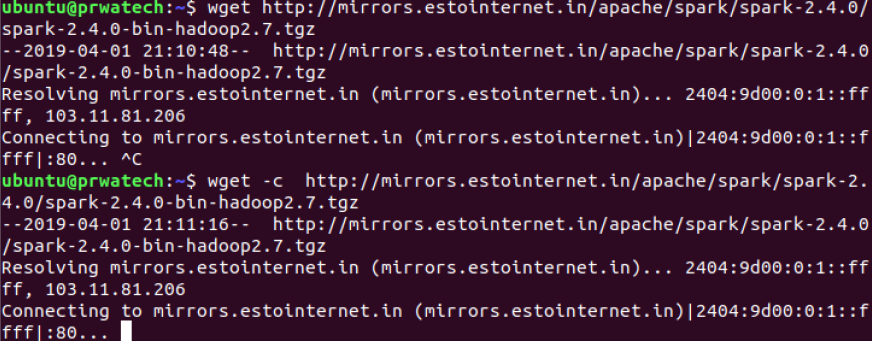
wget -c file ⇒ continue a stopped download
Installation Commands
Install from source:
./configure
make
make install
![]()
dpkg-i pkg.deb ⇒ install a package (Debian)
Shortcuts Commands
♦ Ctrl+C ⇒ halts the current command
♦ Ctrl+Z ⇒ stops the current command, resume with
fgin the foreground or bgin the background
♦ Ctrl+D ⇒ log out of current session, similar to exit
♦ Ctrl+W ⇒ erases one word in the current line
♦ Ctrl+U ⇒ erases the whole line
♦ Ctrl+R ⇒ type to bring up a recent command
♦ !! ⇒ repeats the last command
♦ exit ⇒ log out of current session
Thanks for Reading us, if you are also the one who is keen to learn the technology like a pro from scratch to advanced level, the Ask your World-class Trainers of India’s Leading Hadoop Training institute now and get Benefits of Big Data Certification course from Prwatech.