Hadoop Cluster on Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Hadoop Cluster on Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Hadoop Cluster on Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Welcome to the world of advanced Tutorials on Hadoop. Are you looking forward to Creating a Hadoop Cluster on Google Cloud Platform? Or looking for some help on how to Setup Hadoop on GCP (Google Cloud platform)? Then you’ve landed on the Right Path which providing advanced tutorial Based concepts on the Hadoop cluster. In this tutorial, one can easily explore how to Setup Hadoop on GCP (Google Cloud platform) with step by step explanation.
There are many possible ways to Create Hadoop cluster on GCP Platform, just follow the below-mentioned step by step process of How to Setup Hadoop on GCP (Google Cloud platform) Tutorials which was originally designed by India’s Leading Big Data Training institute Professionals who also offering advanced Hadoop Course and Certification Programs.
Prerequisites
1.GCP Account
2. First Create a GCP Account
3. It’s Free and Google will give you 300$ Credits which is 21 thousand approx.
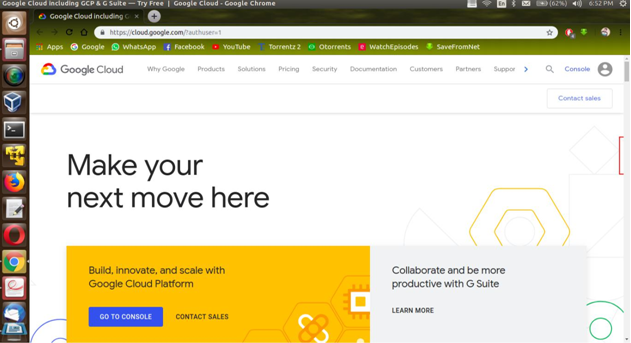
♦ Now Open Google Cloud Platform
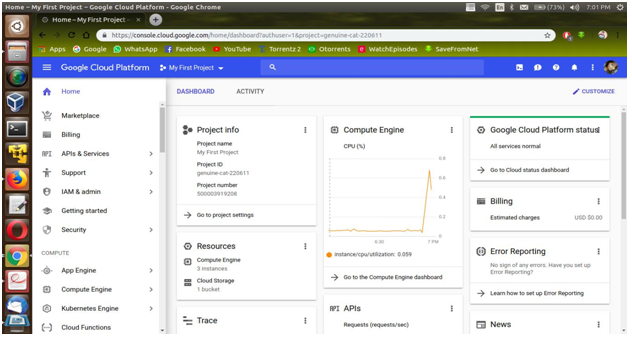
♦ Open Console
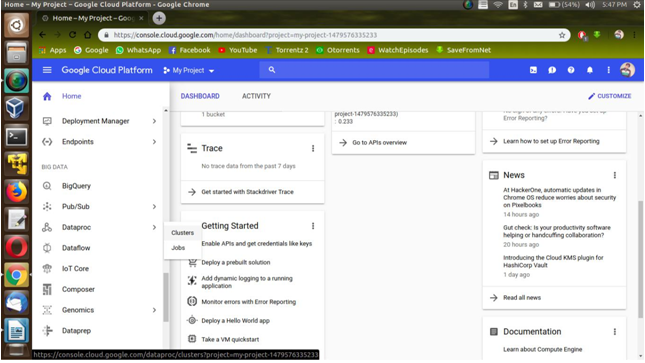
♦ To create instance go to Bigtable from the top bar

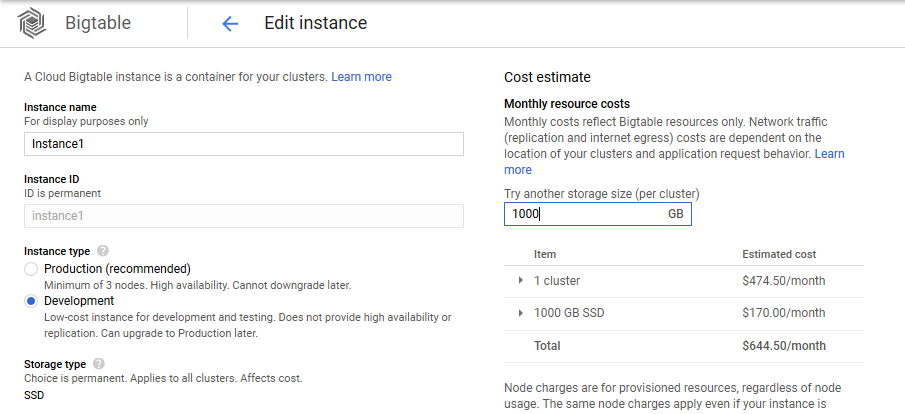
♦ Enter your instance name and choose the instance type (follow below-given configuration)
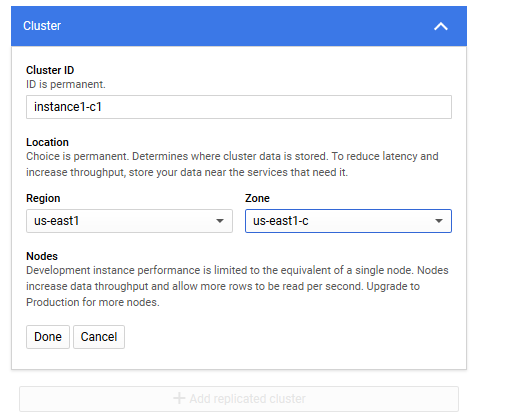
♦ Select region and zone
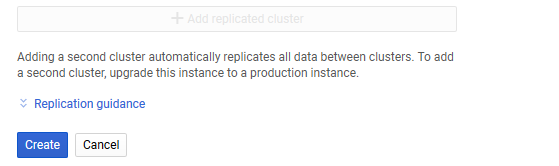
♦ Click on ‘Create’ to create an instance
♦ An instance will be created as per your configuration

♦ Now tap on the console button to open up the terminal

♦ The terminal will be displayed
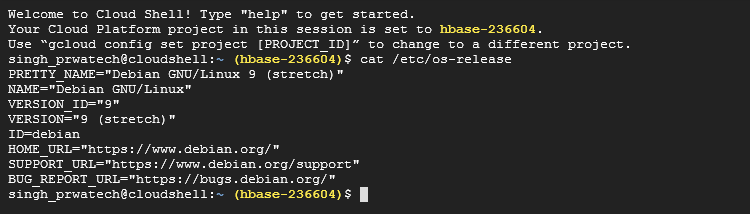
♦ Now check for your system configuration
Command : cat /etc/os-release
Cluster Instance
♦ Go to Dataproc and Click on Cluster
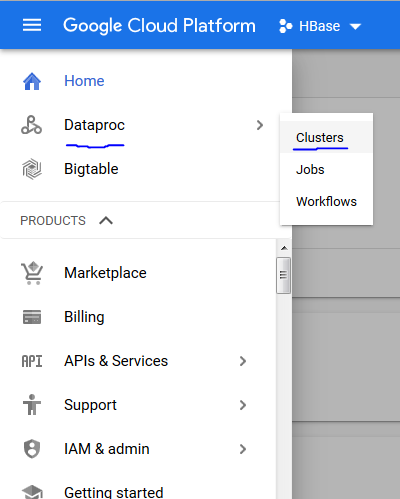
♦ Now Create Cluster
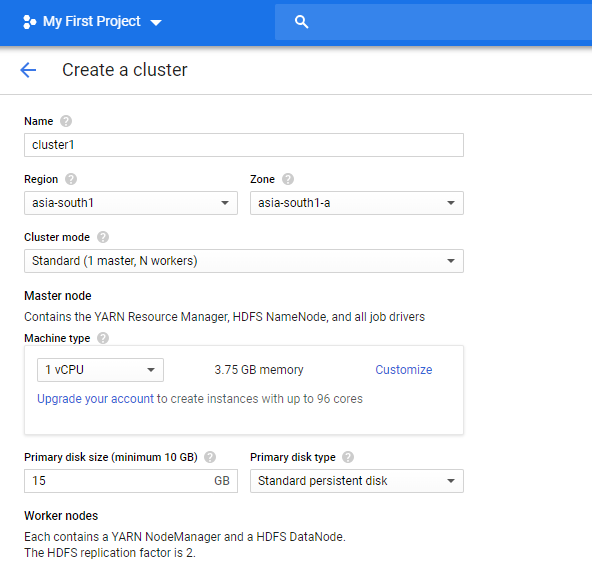
♦ Name Your Cluster and Select Region
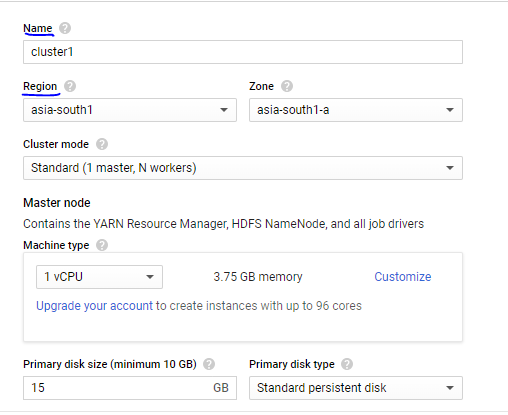
♦ Configure Master and Slave Nodes
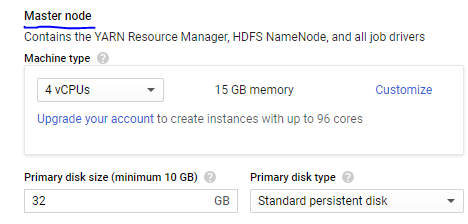
1.Master Node > Machine Type 4 CPUs
2.Primary Disk Size 32GB
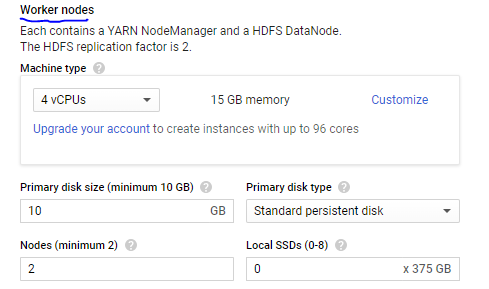
3.Worker Nodes > Machine Type 1
4.CPU > Primary Disk Size 10GB
♦ Click on Advance if you want to add any bucket or select an iso
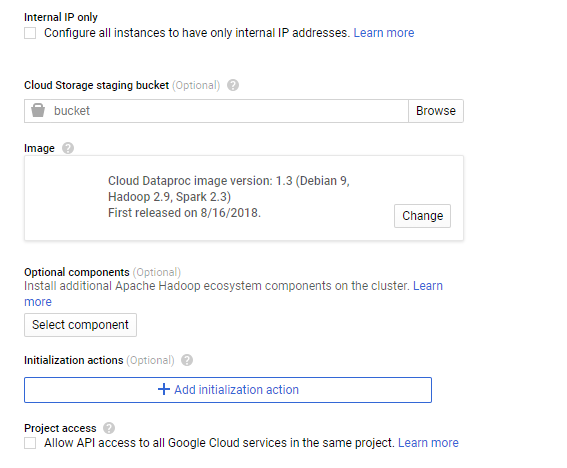
♦ Click on Create
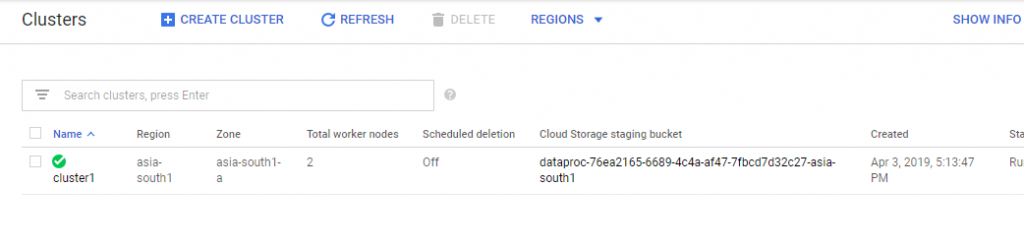
♦ It will take a few seconds. Then you can see the status of the cluster as active and Running
♦ Click on Cluster > VM Instances
♦ Click on SSH
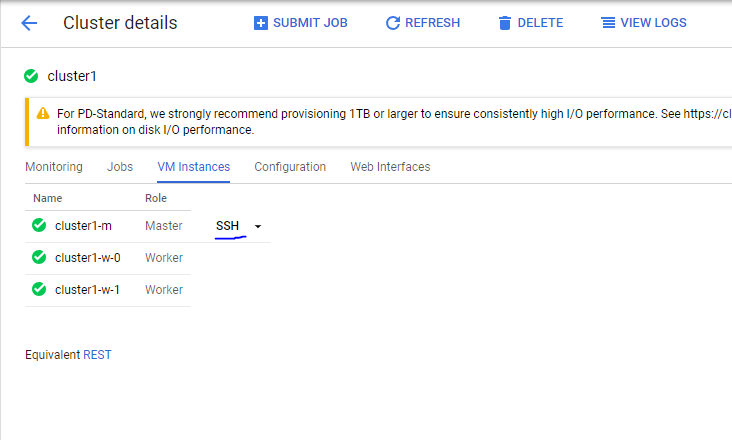
♦ It will start the terminal
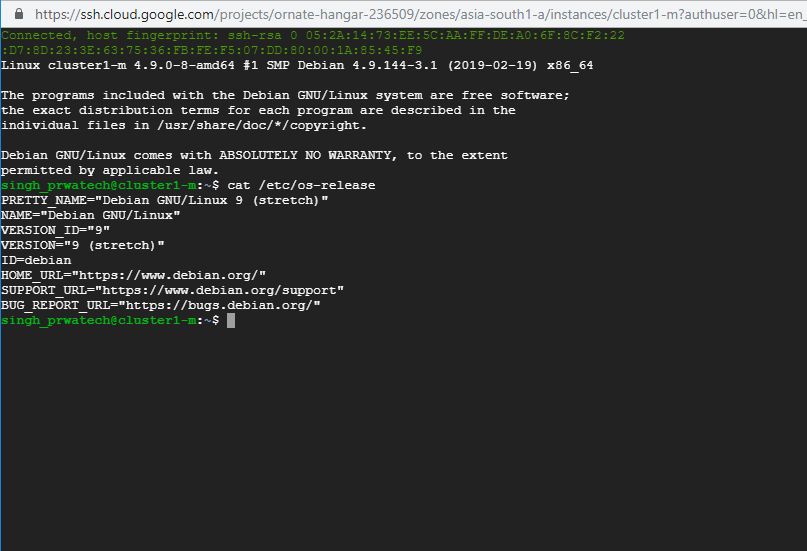
♦ Using Command : cat /etc/os-release
You can see all the details of the Operating System
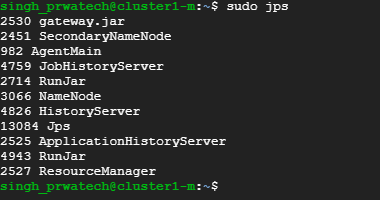
♦ Use the command: Sudo jps
To check for all the running nodes in the cluster