Guide to lazy val in Scala
In Scala Vals and Lazy vals are present . lazy keyword changes the val to get lazily initialized. Lazy initialization means that whenever an object creation seems costly, the lazy keyword can be stick before val. This gives it the advantage to get initialized in the first use i.e. the expression inbound is not evaluated immediately but once on the first access.
In Scala, lazy val is a language feature that delays the initialization of a value until it is accessed for the first time. This allows for deferred computation of values, improving performance and memory usage in scenarios where the value might not always be needed.
When a lazy val is defined, its initialization expression is not evaluated immediately during object creation like a regular val. Instead, the initialization expression is evaluated only when the lazy val is first accessed, and the computed value is stored for subsequent accesses.
The use of lazy val is particularly beneficial for initializing values that are expensive to compute or involve complex initialization logic. By deferring initialization until the value is actually needed, unnecessary computations are avoided, leading to more efficient resource utilization.
It's important to note that lazy val is thread-safe by default, ensuring that the initialization expression is evaluated exactly once, even in concurrent environments.
use case 1:
object prwatech {
// Main method
def main(args:Array[String])
{
lazy val prwatech = {
println ("Initialization for the first time")
2
}
// Part 1
println(prwatech)
// Part 2
print(prwatech)
}
}
Output
Initialization for the first time
2
2
In the code above ‘prwatech’ was a lazy val and so for the first when it is accessed, it returned
Initialization for the first time
2
But for the second time when it is printed, it only returned
2
Because it is a cached result.
use case 2:
object prwatech {
// Main method
def main(args:Array[String])
{
var a = 3
def fun() = {
a += 1;
a
}
lazy val prwatech = Stream.continually( fun() )
(prwatech take 5) foreach {
x => println(x)
}
}
}
output:
4
5
6
7
8use case 3:
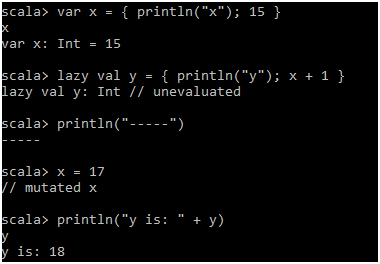
scala>var x = { println("x"); 15 }
scala>lazy val y = { println("y"); x + 1 }
scala>println("-----")
scala>x = 17
scala>println("y is: " + y)
Guide to lazy val in Scala


