Hadoop Basic HDFS Commands
Hadoop Basic HDFS Commands
Hadoop HDFS Commands, welcome to the world of Hadoop HDFS Basic commands. Are you the one who is looking forward to knowing the apache Hadoop HDFS commands List which comes under Hadoop technology? Or the one who is very keen to explore the list of all the HDFS commands in Hadoop with examples that are available? Then you’ve landed on the Right path which provides the standard and Basic Hadoop HDFS Commands.
If you are the one who is keen to learn the technology then learn the advanced certification course from the best Hadoop training institute who can help guide you about the course from the 0 Level to Advanced level. So don’t just dream to become the certified Pro Developer Achieve it by choosing the best World classes Hadoop Training institute which consists of World-class Trainers.
We, Prwatech listed some of the Top Hadoop HDFS Commands which Every Hadoop Developer should know about. So follow the Below Mentioned Hadoop Basic HDFS Commands and Learn the Advanced Hadoop course from the best Hadoop Trainer like a Pro.
Open a terminal window to the current working directory.
==> /home/training

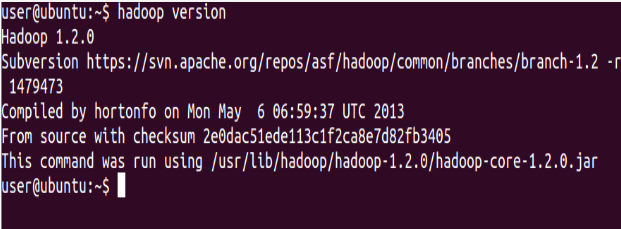
Print the Hadoop version
⇒ Hadoop version
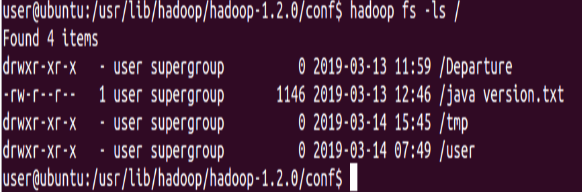
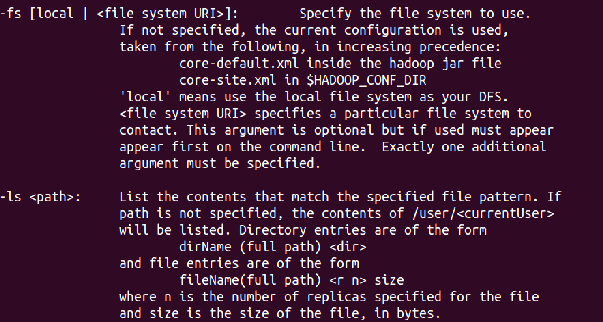
List the contents of the root directory in HDFS
⇒ Hadoop fs -ls /
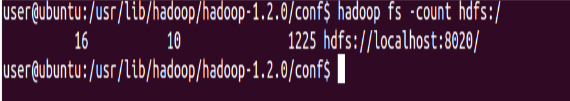
Count the number of directories, files, and bytes under the paths
⇒ Hadoop fs -count hdfs:/
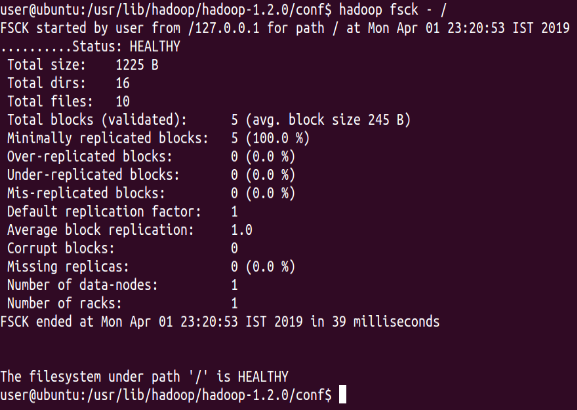
Run a DFS filesystem checking utility
⇒ Hadoop fsck – /
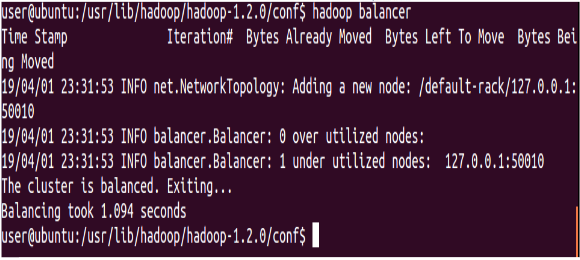
Run a cluster balancing utility
⇒ Hadoop balancer
Create a new directory named “Hadoop” below the /user/training directory in HDFS.
⇒ Hadoop fs -mkdir /user/training/Hadoop

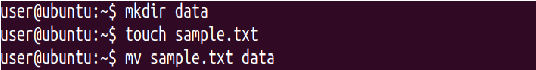
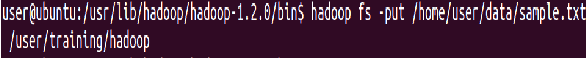
Add a sample text file from the local directory named “data” to the new directory you created in HDFS during the previous step
⇒ Hadoop fs -put data/sample.txt/user/training/Hadoop
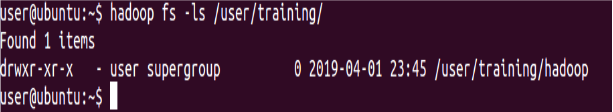
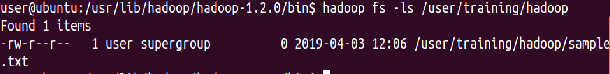
List the contents of this new directory in HDFS
⇒ Hadoop fs -ls /user/training/Hadoop
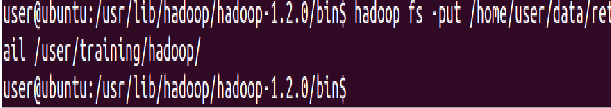
Add the entire local directory called “retail” to the /user/training directory in HDFS
⇒ Hadoop fs -put data/retail /user/training/Hadoop
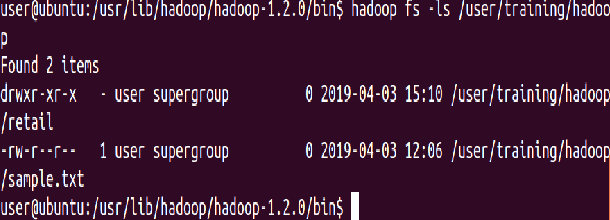
Since /user/training is your home directory in HDFS, any command that does not have an absolute path is interpreted as relative to that directory. The next command will, therefore, list your home directory, and should show the items you’ve just added there
⇒ Hadoop fs -ls
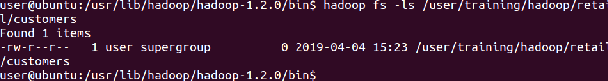
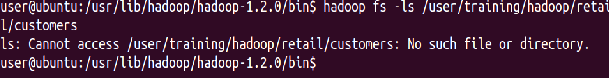
Delete a file ‘customers’ from the “retail” directory
⇒ Hadoop fs -rm Hadoop/retail/customers
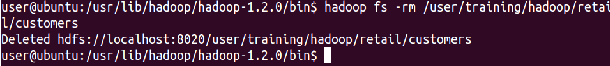
Ensure this file is no longer in HDFS
⇒ Hadoop fs -ls Hadoop/retail/customers
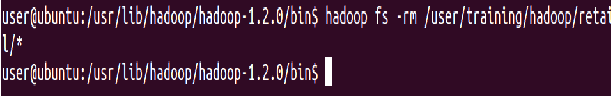
Delete all files from the “retail” directory using a wildcard
⇒ Hadoop fs -rm hadoop/retail/*
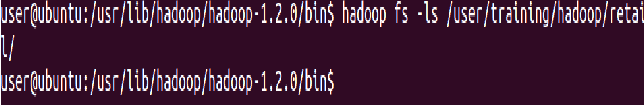
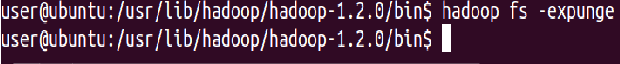
To empty the trash
⇒ Hadoop fs -expunge
Finally, remove the entire retail directory and all
of its contents in HDFS
⇒ Hadoop fs -rm -r Hadoop/retail
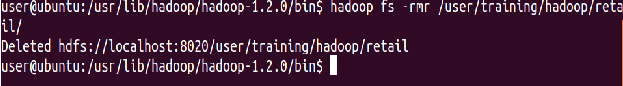
List the Hadoop directory again
⇒ Hadoop fs -ls Hadoop
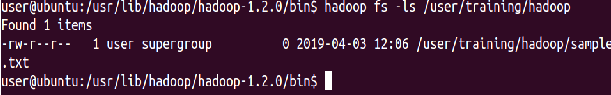
Add the purchases.txt file from the local directory named “/home/training/” to the Hadoop directory you created in HDFS
⇒ Hadoop fs -copyFromLocal /home/training/purchases.txt Hadoop/
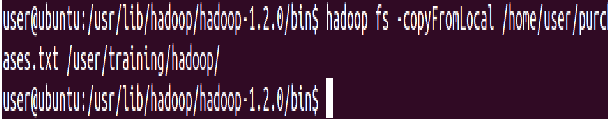
To view the contents of your text file purchases.txt which is present in your Hadoop directory
⇒ Hadoop fs -cat hadoop/purchases.txt
Add the purchases.txt file from “Hadoop” directory which is present in HDFS directory to the directory “data” which is present in your local directory
⇒ Hadoop fs -copyToLocal hadoop/purchases.txt /home/training/data
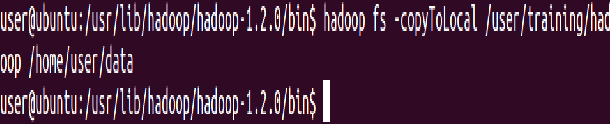
cp is used to copy files between directories present in HDFS
⇒ Hadoop fs -cp /user/training/*.txt /user/training/Hadoop
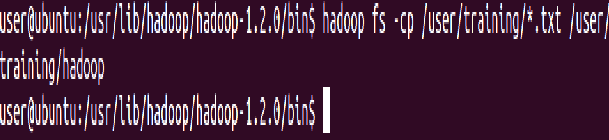
‘-get’ command can be used alternatively to ‘-copyToLocal’ command
⇒ Hadoop fs -get hadoop/sample.txt /home/training/
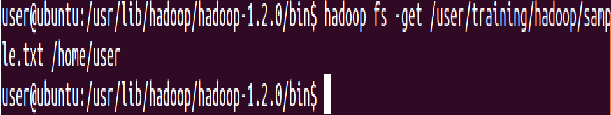
Display last kilobyte of the file “purchases.txt” to stdout
⇒ Hadoop fs -tail hadoop/purchases.txt
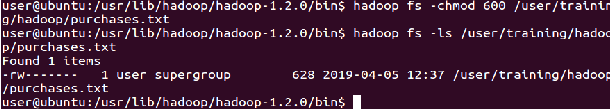
Default file permissions are 666 in HDFS
Use ‘-chmod’ command to change permissions of a file
⇒ Hadoop fs -ls hadoop/purchases.txt
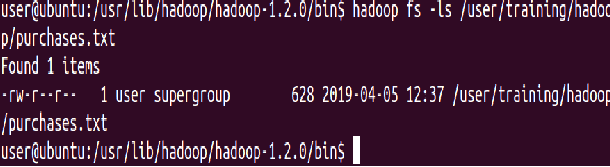
sudo -u hdfs Hadoop fs -chmod 600 hadoop/purchases.txt
Default names of owner and group are training, training Use ‘-chown’ to change owner name and group name simultaneously
⇒ hadoop fs -ls hadoop/purchases.txt
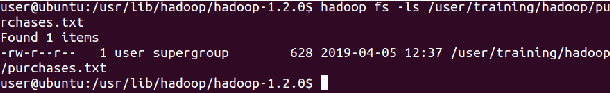
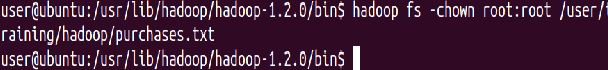
sudo -u hdfs Hadoop fs -chown root: root hadoop/purchases.txt
The default name of group is training Use ‘-chgrp’ command to change the group name
⇒ Hadoop fs -ls hadoop/purchases.txt
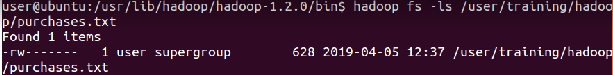
sudo -u hdfs Hadoop fs -chgrp training hadoop/purchases.txt
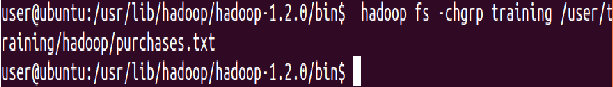
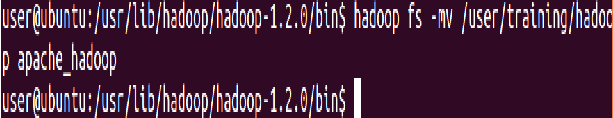
Move a directory from one location to other
⇒ Hadoop fs -mv Hadoop apache_hadoop
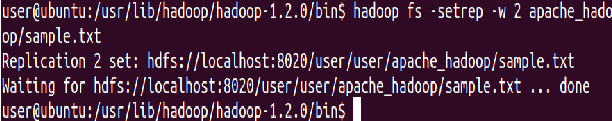
The default replication factor to a file is 3. Use ‘-setrep’ command to change the replication factor of a file
⇒ Hadoop fs -setrep -w 2 apache_hadoop/sample.txt
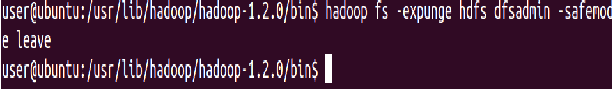
Command to make the name node leave safe mode
⇒ Hadoop fs -expunge sudo -u hdfs hdfs dfsadmin -safemode leave
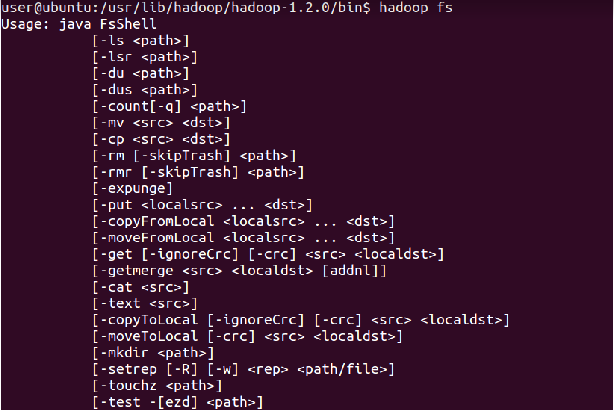
List all the Hadoop file system shell commands
⇒ Hadoop fs
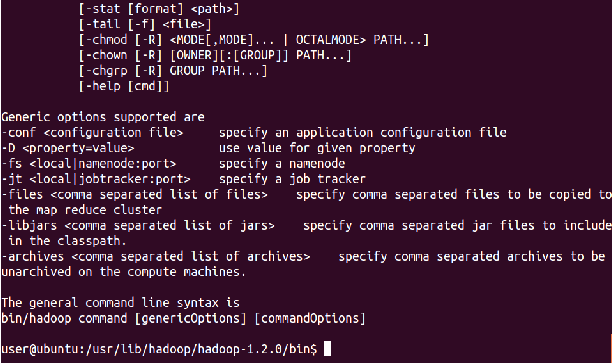
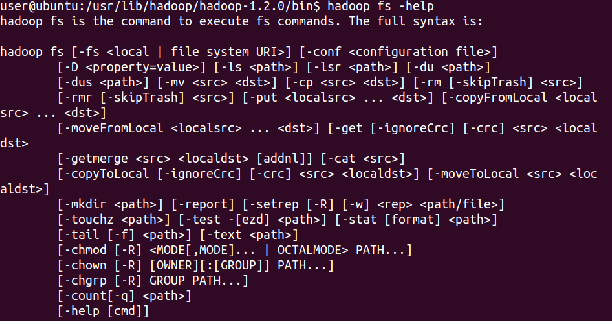
⇒ Hadoop fs -help
I hope you like Prwatech Hadoop Basic HDFS Commands, Get the Advanced certification from World-class Trainers of Best Hadoop Training Institute.
-
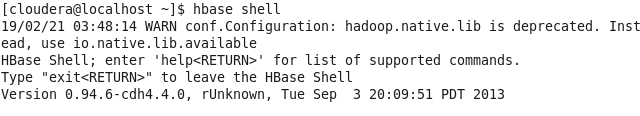
OPEN TERMINAL AND GO TO HBASE SHELL :
cloudera@cloudera-vm:~$ hbase shell
-
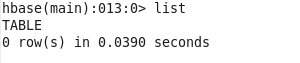
CHECK WHAT TABLES EXISTS IN THE SYSTEM :
hbase(main):001:0> list
TABLE
-
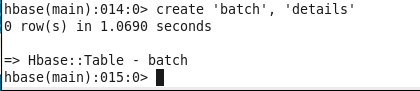
CREATE TABLE :
hbase(main):002:0> create ‘batch’, ‘details’
-
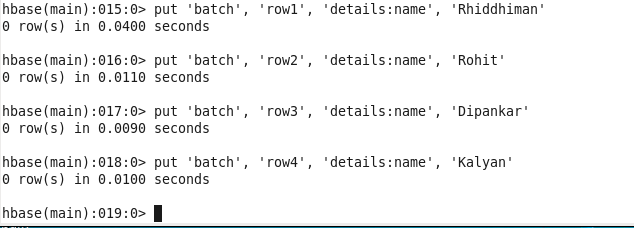
ENTER DATA INTO THE TABLE :
hbase(main):003:0> put ‘batch’, ‘row1’, ‘details:name’, ‘Rhiddhiman’
hbase(main):004:0> put ‘batch’, ‘row2’, ‘details:name’, ‘Rohit’
hbase(main):005:0> put ‘batch’, ‘row3’, ‘details:name’, ‘Dipankar’
hbase(main):006:0> put ‘batch’, ‘row4’, ‘details:name’, ‘Kalyan’
-
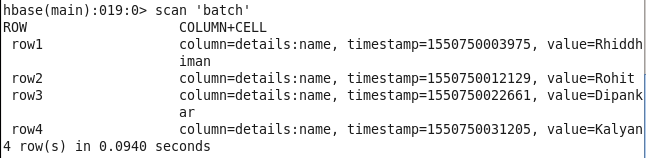
CHECK DATA ENTERED IN THE TABLE :
hbase(main):007:0> scan ‘batch’
-
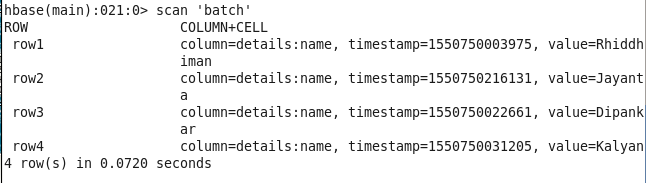
CHANGE VALUE OF A PARTICULAR COLUMN IN A ROW :
hbase(main):008:0> put ‘batch’, ‘row2’, ‘details:name’, ‘Jayanta’
![]()
-
CHECK DATA AFTER MODIFICATION
hbase(main):009:0> scan ‘batch’
-
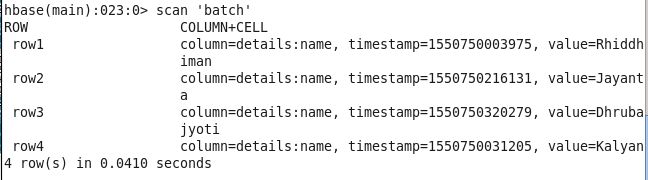
CHANGE VALUE OF A PARTICULAR COLUMN IN A ROW :
hbase(main):010:0> put ‘batch’, ‘row3’, ‘details:name’, ‘Dhrubajyoti’
![]()
-
CHECK DATA AFTER MODIFICATION :
hbase(main):011:0> scan ‘batch’
-
CHECK VALUE THAT HAS BEEN CHANGED :
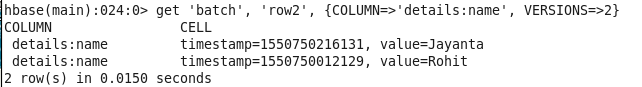
hbase(main):012:0> get ‘batch’, ‘row2′, {COLUMN=>’details:name’, VERSIONS=>2}
hbase(main):013:0> put ‘batch’, ‘row3’, ‘details:name’, ‘Banajit’
![]()
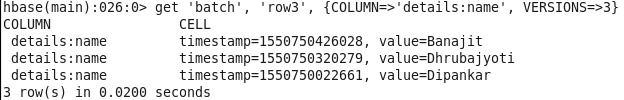
hbase(main):014:0> get ‘batch’, ‘row3′, {COLUMN=>’details:name’, VERSIONS=>3}
-
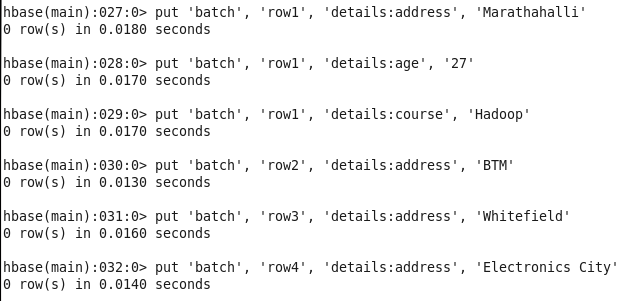
ENTER REMAINING DATA :
hbase(main):015:0> put ‘batch’, ‘row1’, ‘details:address’, ‘Marathahalli’
hbase(main):016:0> put ‘batch’, ‘row1’, ‘details:age’, ’27’
hbase(main):017:0> put ‘batch’, ‘row1’, ‘details:course’, ‘Hadoop’
hbase(main):018:0> put ‘batch’, ‘row2’, ‘details:address’, ‘BTM’
hbase(main):019:0> put ‘batch’, ‘row3’, ‘details:address’, ‘Whitefield’
hbase(main):020:0> put ‘batch’, ‘row4’, ‘details:address’, ‘Electronics City’
-
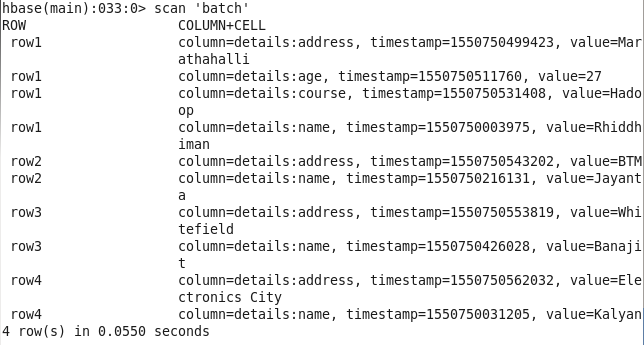
CHECK DATA :
hbase(main):021:0> scan ‘batch’
-
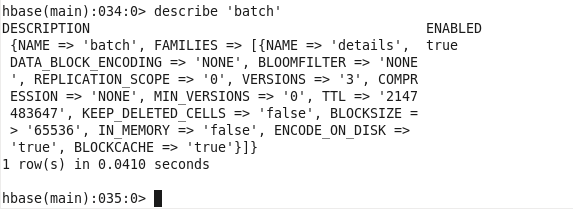
DESCRIPTION OF TABLE :
hbase(main):031:0> describe ‘batch’