scala First class function
In functional programming, functions are assign to variables, pass to other functions as parameters, and return as values from other functions. Such functions are as First Class Functions.
In Scala, functions are consider first-class citizens, which means they can be treat just like any other value, such as integers or strings. This powerful feature enables functional programming paradigms where functions can be pass as arguments to other functions, return from functions as results, and assign to variables.
Scala’s support for first-class functions allows for concise and expressive code, promoting modular and reusable patterns. Functions can be defined using function literals ((parameters) => expression) or as named functions using the def keyword.
First-class functions enable higher-order functions, which are functions that take other functions as parameters or return functions as results. This higher-order function capability facilitates common functional programming patterns such as map, filter, reduce, and more.
Scala’s support for first-class functions is integral to its functional programming capabilities, enabling developers to write elegant and composable code. By leveraging first-class functions, developers can design more flexible and maintainable systems that embrace functional programming principles. This feature is particularly useful for asynchronous programming, event handling, and concurrency patterns in Scala applications. scala First class function
Use case 1:
Assign function as Variable
scala>(i:Int) => {i*2}
scala>val doubler = (i:Int) => {i*2}
scala>doubler(5)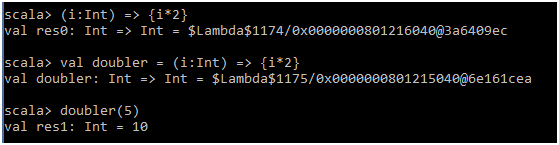
2Use case 2:
Pass function as Parameter
scala>def operation(functionparam:(Int, Int) => Int){
println(functionparam(10,5))
}
scala> val sum = (x:Int, y:Int)=> x+y
scala>operation(sum);
scala>val diff = (x:Int, y:Int)=> x-y
scala>operation(diff);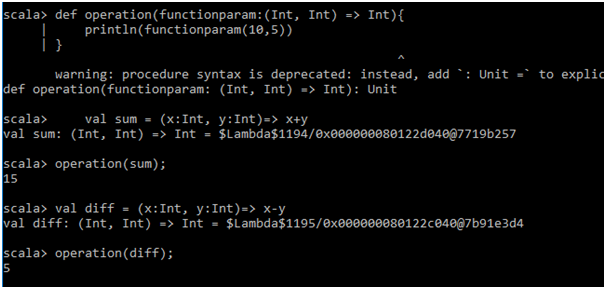
Use case 3:
Return a Function
object prwatech {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val doubleValue = doubler();
print("Double of 2 = " + doubleValue(2));
}
def doubler() = (num: Int) => num * 2;
}
Output
Double of 2 = 4


