Creating a List in Scala
List:
All the elements of a list have the same type but there are two important differences. First, lists are immutable, which means elements of a list cannot be changed by assignment. Second, lists represent a linked list whereas arrays are flat.
In Scala, lists are immutable collections that represent ordered sequences of elements. To create a list in Scala, you can use the List companion object to instantiate a new list with specified elements. Lists in Scala are implemented as linked lists, where each element is stored in a node that points to the next element in the list.
Here’s how you can create a list in Scala:
// Creating a list of integers
val numbers: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
// Creating a list of strings
val fruits: List[String] = List(“apple”, “banana”, “orange”)
Run the following commands:
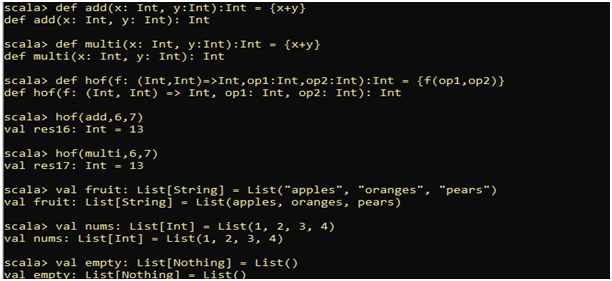
· By default immutable
They do not maintain order
· List can’t be accessed by their Index.
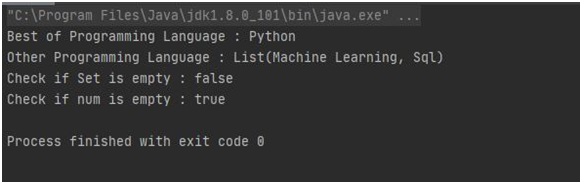
1. Example program to show usage of the basic List operational methods:
package Collection
object List1 {
defmain(args: Array[String]) {
val lang1 = "Python" :: ("Machine Learning" ::( "Sql"::
1Nil
)) val num =
Nil println
( "Best of Programming Language : " + lang1.head )
println
( "Other Programming Language : " + lang1.tail )
2println
( "Check if Set is empty : " + lang1.isEmpty )
println
( "Check if num is empty : " + num.
isEmpty
) } }
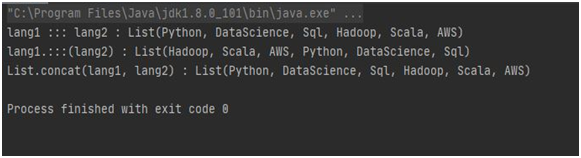
2. Example program to show usage of the List with respect to concatenation:
package Collection
object List2 {
defmain(args: Array[String]) {
val lang1 = "Python" :: ("DataScience"::("Sql"::
2Nil
))
val lang2 = "Hadoop" :: ("Scala" :: ("AWS"::
Nil
)) // using two Lists with ::: as operator var lang = lang1 ::: lang2
println
( "lang1 ::: lang2 : " + lang ) // using two Lists with Set .:::() method lang = lang1.:::(lang2)
3println
( "lang1.:::(lang2) : " + lang ) // passing two lists as arguments lang =
List
.concat(lang1, lang2)
println
( "List.concat(lang1, lang2) : " + lang ) } }
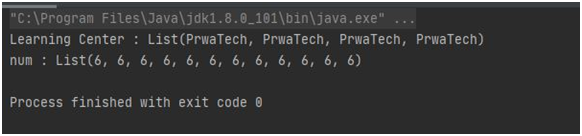
3. Program to create a list with zero or more copies of the same element using List.fill() method.
package Collection
object List3 {
defmain(args: Array[String]) {
// Repeatedly prints PrwaTech four times.
val center =
List
.fill(4)("PrwaTech")
println
( "Learning Center : " + center ) // Repeatedly prints 6, 12 times. val num =
List
.fill(12)(6)
println
( "num : " + num ) } }
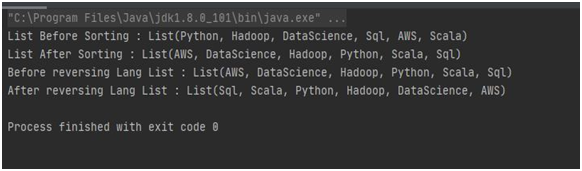
4. Program to Sort and reverse all elements of the list.
package Collection
object List4 {
defmain(args: Array[String]) {
val lang1 = "Python" :: ("Hadoop" :: ("DataScience" :: ("Sql" :: ("AWS" :: ("Scala" ::
Nil
))))) val lang2 = lang1.sorted
("List Before Sorting : " + lang1)
3println
("List After Sorting : " + lang2)
("Before reversing Lang List : " + lang2)
4println
("After reversing Lang List : " + lang2.reverse)
}
}
Creating a List in Scala


