Hadoop Basic PIG Commands with Examples
Hadoop Basic PIG Commands with Examples, are you looking for a list of Top Rated Pig commands in Hadoop examples? Or the one who is casually glancing for the best platform which is listing the Top-rated Hadoop pig script commands with examples for beginners? Then you’ve landed on the Right Platform which is packed with Tons of Tutorials of Pig commands for Hadoop. Follow the below mentioned Pig commands in Hadoop which were originally designed by the world-class Trainers of Big Data Training institute Professionals. If you are the one who is a hunger to become the certified Pro Hadoop Developer? Or the one who is looking for the best Hadoop Training institute which offering advanced tutorials and Hadoop certification course to all the Tech Enthusiasts who are eager to learn the technology from 0 Level to Advanced Level.Basic PIG commands in Hadoop

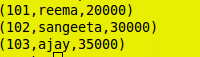
- Create the following input file (text format)
Database 1: studb

Database 2: empdb

#Database 3: detaildb

Database 4: stu2db

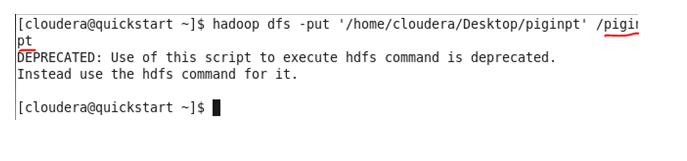
Move the created file from LFS to HDFS
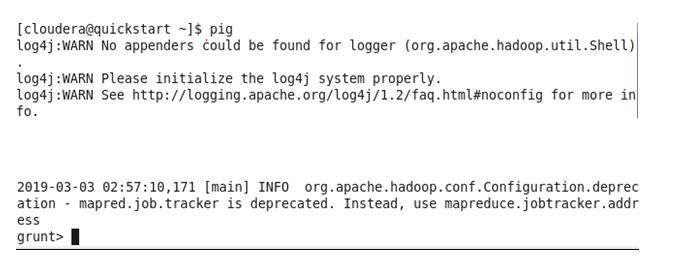
Run PIG command from console (cluster mode)
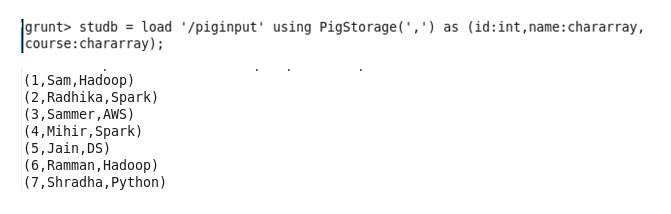
Data Input using pig: Load data from hdfs to Pig
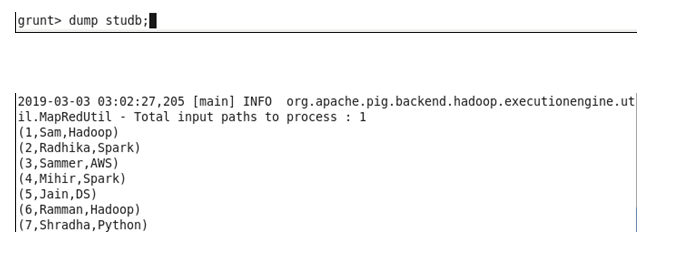
Dump Command: This command is used to display all data loaded.
Foreach: This command is used to generate data transformation based on columns of data


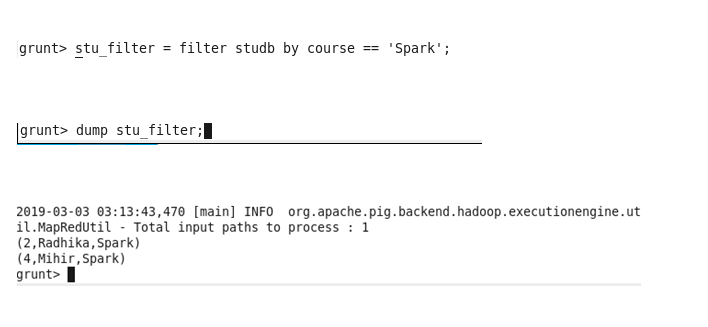
Filter: Select particular tuples from a relation based on a condition.
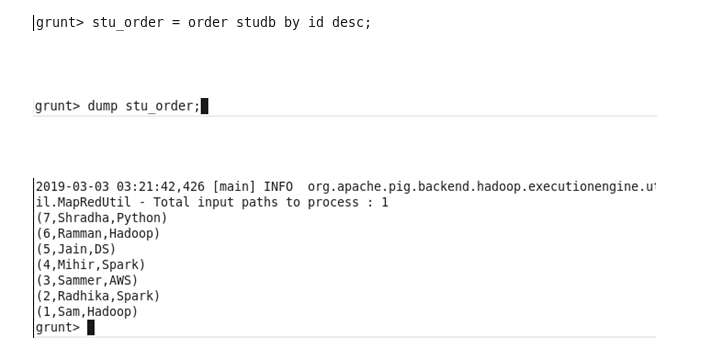
Order By: Sort a relation based on one or more fields
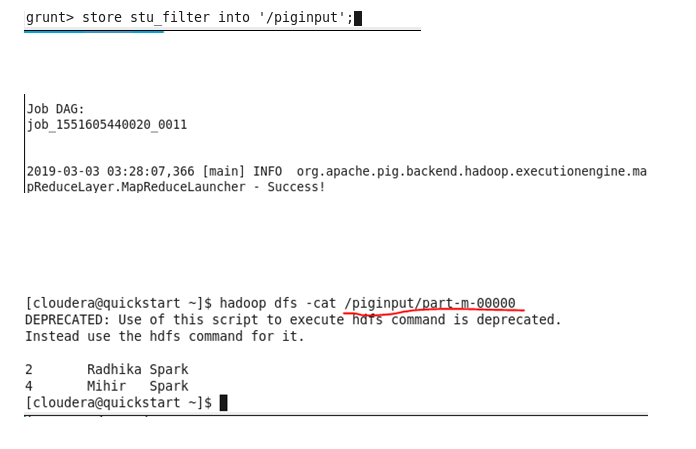
Store: Save results to the local file system or HDFS
Cogroup: This operator is used to group two databases using a particular column.

Pig commands in Hadoop with examples
Join: This operator is used to join two or more table.
Inner Join: Joining two table having a common column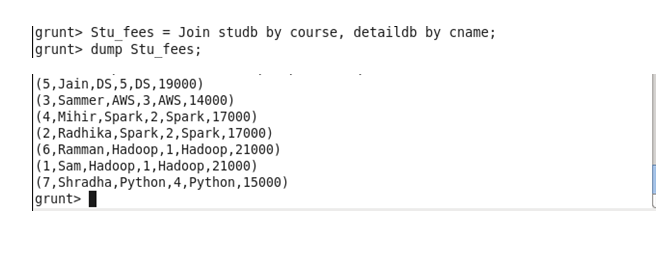 Left Outer: The left outer Join operation returns all rows from the left table, even if there are no matches in the right relation
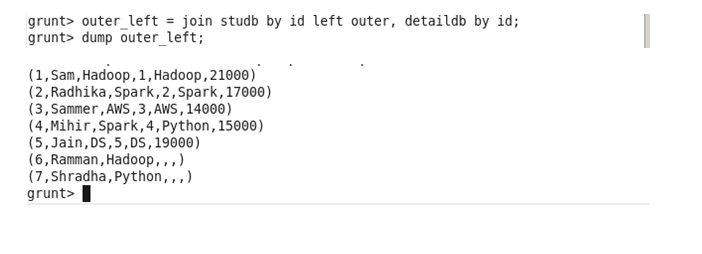
Left Outer: The left outer Join operation returns all rows from the left table, even if there are no matches in the right relation
 Right Outer: The right outer join operation returns all rows from the right table, even if there are no matches in the left table.
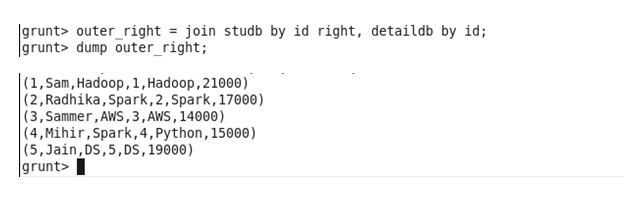
Right Outer: The right outer join operation returns all rows from the right table, even if there are no matches in the left table.
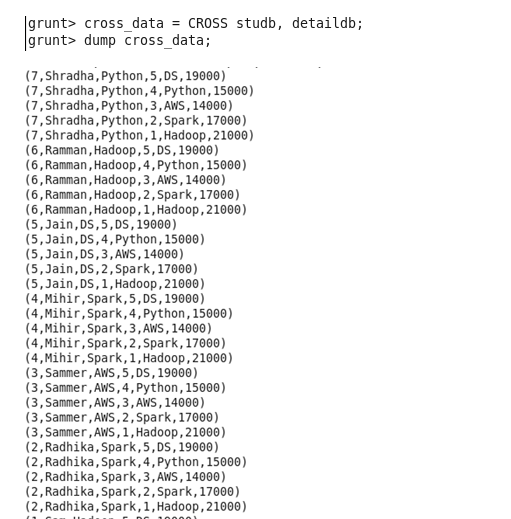
 Cross: The CROSS operator computes the cross-product of two or more relations.
Cross: The CROSS operator computes the cross-product of two or more relations.
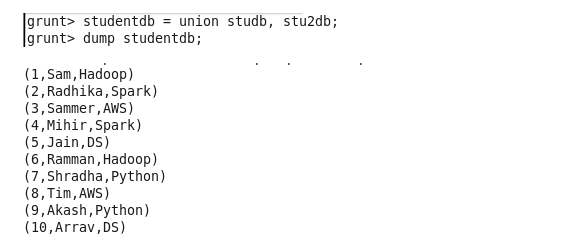
 Union: The UNION operator of Pig Latin is used to merge the content of two relations.
Union: The UNION operator of Pig Latin is used to merge the content of two relations.
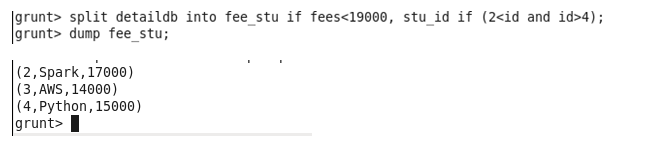
 Split: The split operator is used to split a relation into two or more relations.
Split: The split operator is used to split a relation into two or more relations.
PIG Commands with Examples
GROUP OPERATOR:
The simpler of these operators is GROUP. Continuing with the same set of relations
grunt> Emp_grouped = GROUP Emp BY salary;
 grunt> DUMP Emp_grouped;
grunt> DUMP Emp_grouped;
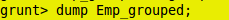
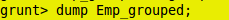
Group Output:

FOREACH OPERATOR:
One of the key uses of Pig is data transformation. You can define a new relation based on the fields of an existing relation using the FOREACH command
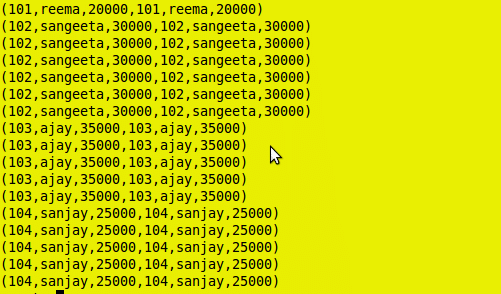
grunt> foreach_Emp = FOREACH Emp GENERATE id,name;
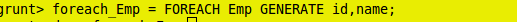
grunt> dump foreach_Emp;
 Foreach Output:
Foreach Output:

 Foreach Output:
Foreach Output:

JOIN OPERATOR:
which groups together tuples from multiple relations . It functions much like a join. For example, let’s Join Emp and Customer on the first column.
grunt> Emp_self = join Emp by id, Customer by id;
grunt> DUMP Emp_self;

Self Join Output:
By default behavior of join as an outer join, and the join keyword can modify it to be left outer join, right outer join, or inner join.Another way to do inner join in Pig is to use the JOIN operator. Empcust_left = join Emp by id left outer, Customer by id;
grunt> dump Empcust_left;
Left Outer Join Output:

Empcust_right = join Emp by id right outer, Customer by id;
grunt> dump Empcust_right;
Right Outer Join Output:
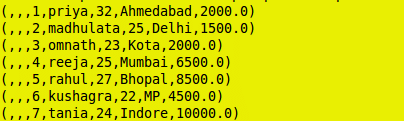
Empcust_full = join Emp by id full outer, Customer by id;
grunt> dump Empcust_full;
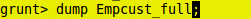
Full Outer Join Output:
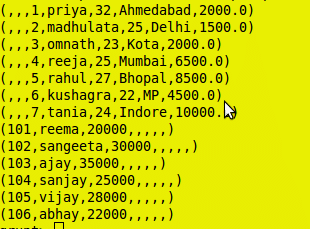
DISTINCT OPERATOR:
grunt> Emp2_dist = DISTINCT Emp2;

grunt> dump Emp2_dist;
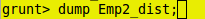
DISTINCT Output:
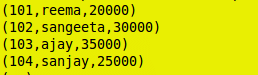
LIMIT OPERATOR:
grunt> limit_data = LIMIT Emp 3;
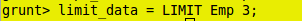
grunt> dump limit_data;
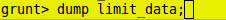 LIMIT Output:
LIMIT Output: