DOCUMENT API’s
- Add Document
Documents in Elasticsearch are stored as a JSON object. Also, documents are added to indices, and documents have a type. One Index can have many types & you can store any number of documents in an Index.
In this example, ” information”, “person” and “1” are index, type and id respectively, Elasticsearch will automatically create the index if it does not exist.
Example:-
POST /information/person/1
{
“name” : “Paul”,
“lastname” : “Wheeler”,
“job_desc” : “Manager”
}
- Get Document
Now that the document is stored, to retrieve the document we use the below API.
Example:- GET /information/person/1
- Update Document
To update a document we use below API.
Example:- POST /information/person/1/_update
{
“doc”:{
“job_description” : “Data analyst”
}
}
- Delete Document
To delete a document use the below API.
Example:-
DELETE /information/person/1
- Search Document
We can search the stored document using either “/_search?q=something”.
Example:-
GET localhost:9200/_search?q=Paul
►Analysis Phase In ElasticSearch
Elasticsearch uses a special data structure called “Inverted index” for very fast searches. An inverted index is a list of all the unique words that a document contains, and for each word, a list of the documents in which it appears. An inverted index is created from a document indexed in elasticsearch. the process of creating an Inverted index from a document called analysis (tokenization and Filterization).
Analysis happens during Indexing a document as well as Searching a document. We will see how elasticsearch creates an Inverted index and how it is stored in shards which later used for searching documents.
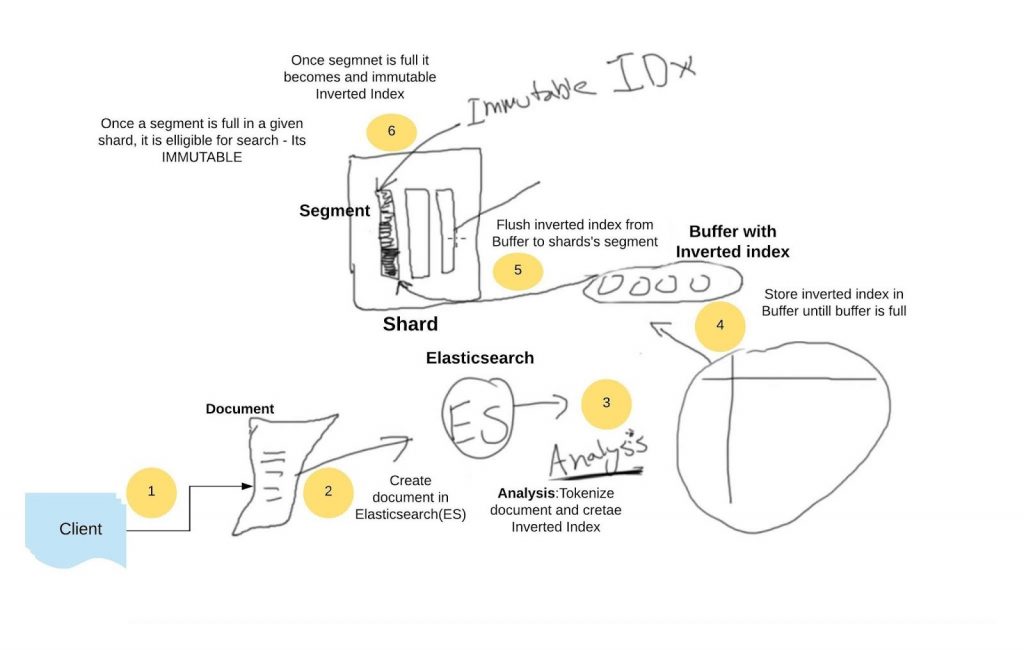 ►The analysis process is the key phase in creating an inverted index in shards. whenever you index a document in Elasticsearch, it goes through the analysis phase where documents are tokenized, filtered processed (stemming, synonyms detected and remove stop words).
►The analysis process is the key phase in creating an inverted index in shards. whenever you index a document in Elasticsearch, it goes through the analysis phase where documents are tokenized, filtered processed (stemming, synonyms detected and remove stop words).
►For every document, this inverted index will be created and stored in a temporary buffer until it becomes full. Once the buffer is full, it is flushed into segments.
►A segment is the smallest logical unit of a Shard basically small blocks where you can store a list of the inverted index. Shard is like a collection of segments. Segments are filled with a flushed inverted index.
►Once a segment is filled completely with an inverted index, shards become eligible for searching. Segments created are an immutable collection of the immutable inverted index.
EXAMPLE: Consider two documents text below for analysis.
Here, we’re indexing these documents to ELS.
POST /user/tweets/
{ “ name”: “Rohit”
“ comment”: “The thin lifeguard was swimming in the lake.”
“ date”: “2018-10-27” }
{ “ name”: “Amol”
“ comment”: “Swimmers race with the skinny lifeguard in the lake”
“ date”: “2018-10-28” }
Let’s assume we are interested in the comment fields of a document. We have two texts to consider for analysis.
1. The thin lifeguard was swimming in the lake
2. Swimmers race with the skinny lifeguard in lake
►Tokenization: To create an inverted index, we simply split the comment of each document into separate words (which we call terms or tokens), creates a sorted list of all the unique terms, along with the list in which document each term/token appears.
| Token | Present in Document |
| Swimmers | 2 |
| The | 1 |
| in | 1,2 |
| lifeguard | 1,2 |
| lake | 1,2 |
| race | 2 |
| skinny | 2 |
| swimming | 2 |
| the | 1,2 |
| thin | 1 |
| was | 1 |
| with | 1 |
►Filtering: After the tokenization filtering process is applied to these. Filters are such as:
►Removing stop words (a, an, the, in, etc. of the English word)
►Lowercasing (To make search case insensitive)
►stemming (swimming to swim)
►synonymous ( thin == skinny )
After these operations, the output which is an inverted index is pushed into buffer.
►ANALYSERS In ElasticSearch
Elasticsearch provides pre-builtin analyzers which can be used in any index without further configuration. Here is a list of elastic search built-in analyzers.
- Standard Analyzer (Default)
- Simple Analyzer
- Whitespace Analyzer
- Stop Analyzer
- Keyword Analyzer
- Pattern Analyzer
- Language Analyzers (English, Hindi, French, Spanish & many more)
- Custom Analyser (we can define our own custom analyzer as well)
♦Bulk Load in ElasticSearch
Bulk load is nothing but indexing/inserting more than one documents at a time.
We have to use the _bulk keyword to upload bulk data.
Example.
(this command will index these 3 documents into vehicles index inside cars type.)
POST /vehicles/cars/_bulk
{ “index”: {}} //index for doc 1
{ “price” : 10000, “colour” : “white”, “make” : “Honda”, “sold” : “2016-10-28”, “condition”: “okay”}
{ “index”: {}} //index for doc 2
{ “price” : 20000, “colour” : “white”, “make” : “Honda”, “sold” : “2016-11-05”, “condition”: “new”}
{ “index”: {}} //index for doc 3
{ “price” : 30000, “colour” : “green”, “make” : “ford”, “sold” : “2016-05-18”, “condition”: “new”}