Scala – Literals
Scala Literals with Examples
Scala literals are representations of constant values in code that have a specific syntax and type associated with them. Scala supports a variety of literals for different types of data, providing flexibility and expressiveness in representing values.
-
Numeric Literals: Scala supports integer literals (
Int,Long,Short,Byte), floating-point literals (Float,Double), and hexadecimal literals (0xprefix). -
String Literals: Scala string literals can be enclosed in double quotes (
"Hello, Scala!") or triple quotes ("""Multiline string"""), supporting escape sequences and interpolation. -
Boolean Literals: Scala has
trueandfalseliterals representing boolean values. -
Symbol Literals: Scala symbols are literals prefix with a single quote (
'symbolName), representing unique identifiers. -
Character Literals: Scala character literals are enclosed in single quotes (
'a','\n'), supporting escape sequences. -
Multiline String Literals: Scala supports multiline string literals using triple quotes (
"""..."""), preserving line breaks and supporting escape sequences. -
Raw String Literals: Scala raw string literals (
raw"...") treat backslashes literally, useful for regular expressions and file paths.
The literals are a series of symbols utilize for describing a constant value in the code.
Types of Literals
Integer Literals: The Integer literals are generally of type Int or of type Long when a suffix L or l is add at the end of the Integers.
Run the following example for Integer Literals:
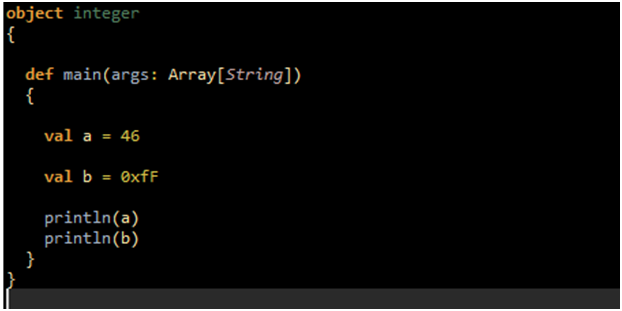
OUTPUT:

Floating Point Literals : This type of literals are of type Double as well as type Float .
Run the following example for Floating Point Literals:
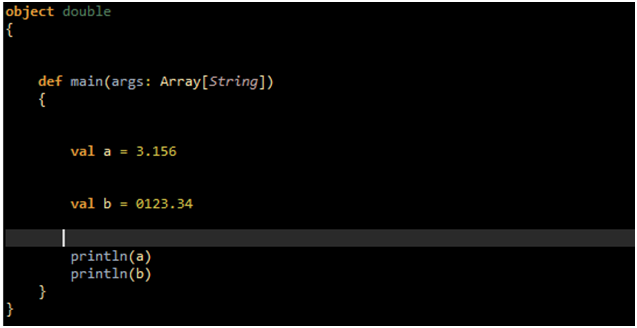
OUTPUT:

Character Literals : They are either uni-code character which are printable or are represent by escape sequences.
Run the following example for Character Literals:
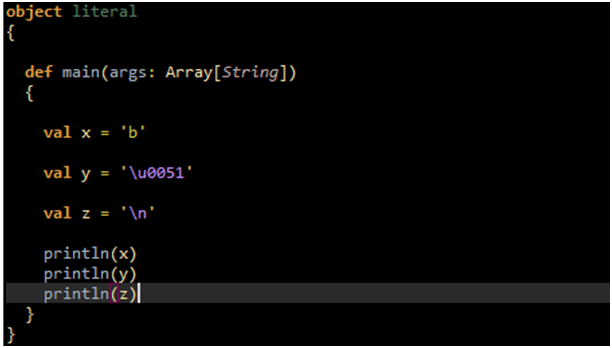
OUTPUT:

String literals : The String literals are series of characters, which are available in double quotes.
Run the following example for String Literals:
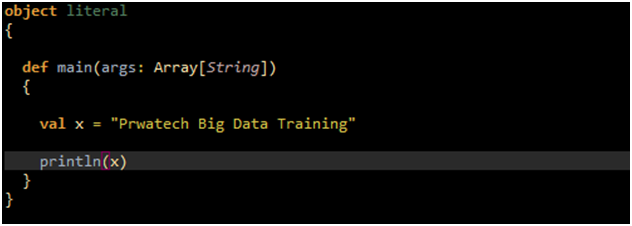
OUTPUT:

Multi-Line String Literals : The multi-line string literals are also series of characters but it has multiple lines.
Run the following example for Multi-Line String Literals :
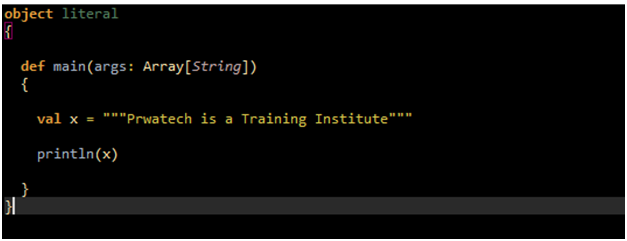
OUTPUT:

Scala Literals with Examples