Azure Storage Redundancy(High Availability)
Azure Storage Redundancy(High Availability)
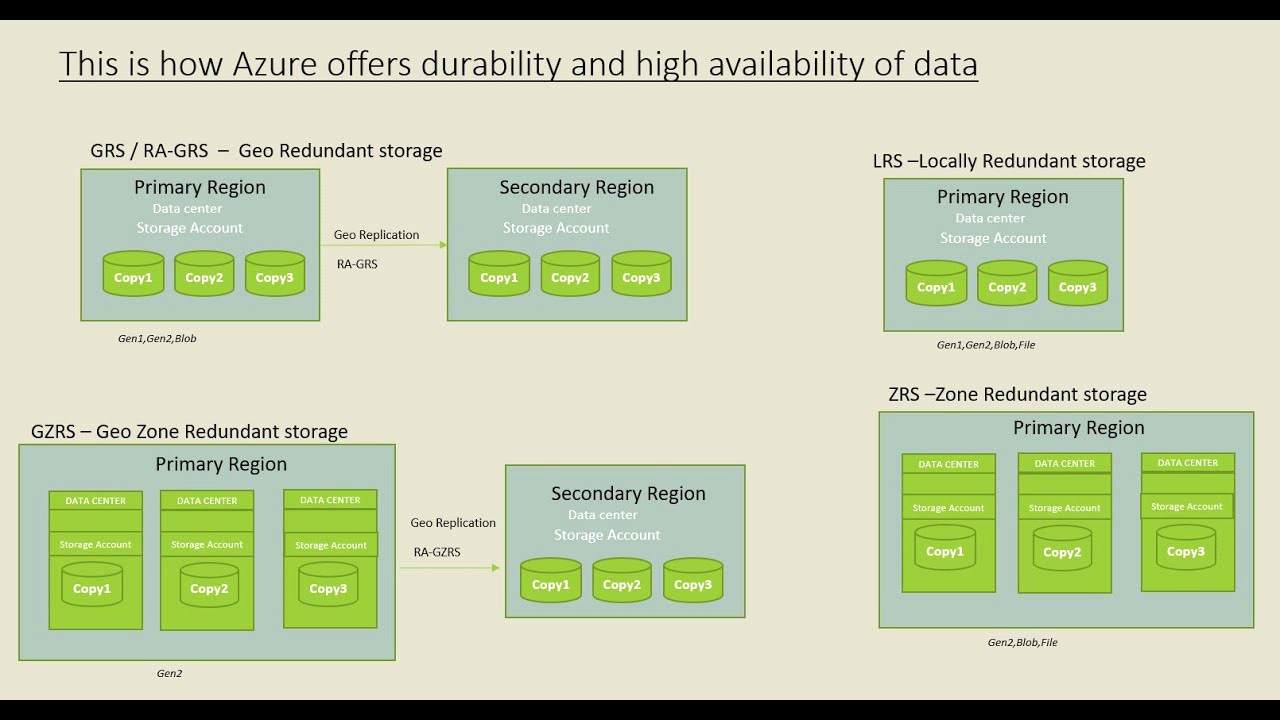
Azure Storage offers several redundancy options to ensure the high availability and durability of data. These redundancy options allow you to choose the level of redundancy based on your application’s requirements, balancing cost and resilience. Here are the primary redundancy options available in Azure Storage:
- Locally Redundant Storage (LRS):
- LRS replicates your data within a single storage scale unit (rack) in a data center.
- It provides at least three copies of your data within the same region but in different fault domains to protect against hardware failures.
- LRS is the most cost-effective redundancy option but offers the lowest durability compared to other options.
- Geo-Redundant Storage (GRS):
- GRS replicates your data synchronously to a secondary region hundreds of miles away from the primary region.
- In case of a regional outage or disaster, your data remains available from the secondary region.
- Zone-Redundant Storage (ZRS):
- ZRS replicates your data across availability zones within the same region.
- Availability zones are physically separate data centers with independent power, cooling, and networking.
- ZRS provides higher availability than LRS because it protects against data center failures within the region.
- Read-Access Geo-Redundant Storage (RA-GRS):
- RA-GRS provides the same redundancy as GRS but also allows read access to data in the secondary region.
- This allows you to access your data from the secondary region for read operations, providing additional redundancy and reducing latency for read-intensive workloads.
- Zone-Redundant Storage Plus (ZRS+):
- ZRS+ is an extension of ZRS that also replicates data to a secondary region for added redundancy.
- It combines the benefits of ZRS (high availability within the region) with the added protection of geo-redundancy.
- ZRS+ is suitable for mission-critical applications that require both high availability and data protection across regions.
0
0