Variables & Operators in Golang
Variables & Operators in Golang
In Golang (or Go), variables are used to store and manipulate data within programs. They are defined using the `var` keyword followed by the variable name and type. For example, `var age int` declares a variable named `age` of type `int`. Golang supports various data types including integers (`int`, `int8`, `int16`, `int32`, `int64`), floating-point numbers (`float32`, `float64`), strings (`string`), booleans (`bool`), and more.
Operators in Golang are symbols or keywords used to perform operations on variables and values. Golang supports arithmetic operators (`+`, `-`, `*`, `/`, `%`), comparison operators (`==`, `!=`, `<`, `<=`, `>`, `>=`), logical operators (`&&`, `||`, `!`), assignment operators (`=`, `+=`, `-=`, `*=`, `/=`), and more. For example, `a + b` performs addition, `x > y` checks if `x` is greater than `y`, and `!flag` negates the value of `flag`.
Golang also provides special operators like `&` (address operator), `*` (pointer dereference operator), `++` and `–` (increment and decrement operators), and `:=` (short variable declaration). Understanding variables and operators is essential for writing efficient and concise Golang code, enabling developers to manipulate data and perform computations effectively within their programs.
Prerequisites
Hardware : Local Machine
Software : VS Code, Golang
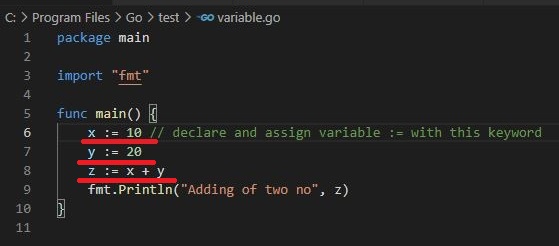
Variable Declaration
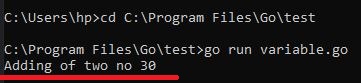
Output :
Variable declaration with var keyword.
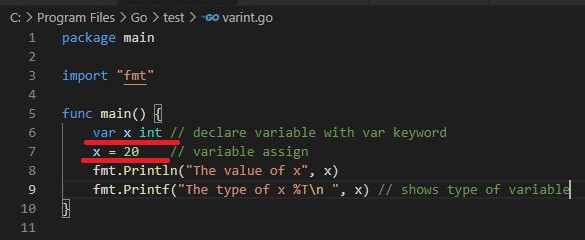
Output :
Mixed variable declare
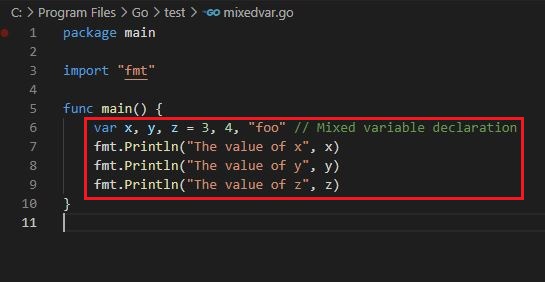
Output :
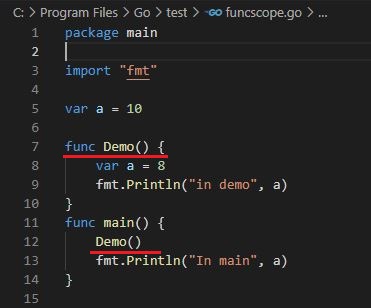
Scope of variable
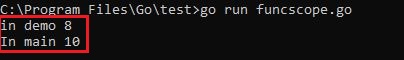
Output :
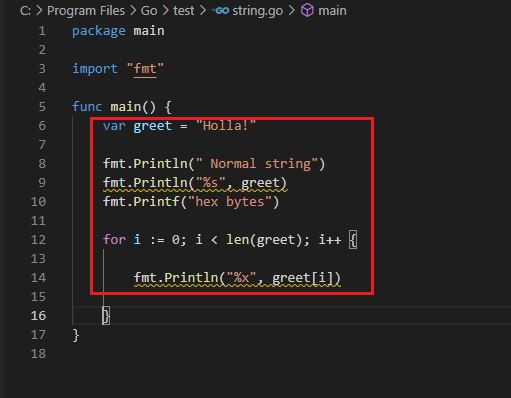
String declaration
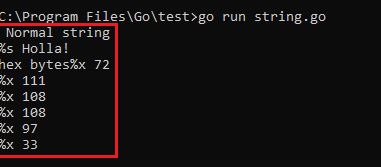
Output :
Operators
Using * operator [Multiply]
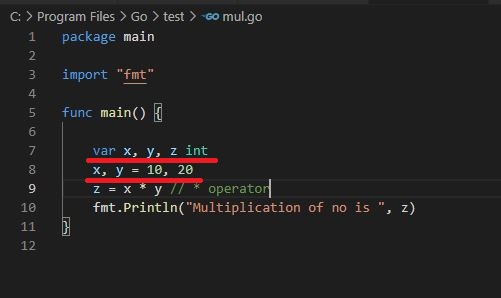
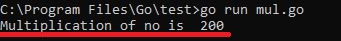
Output :
Logical AND operator [&&]
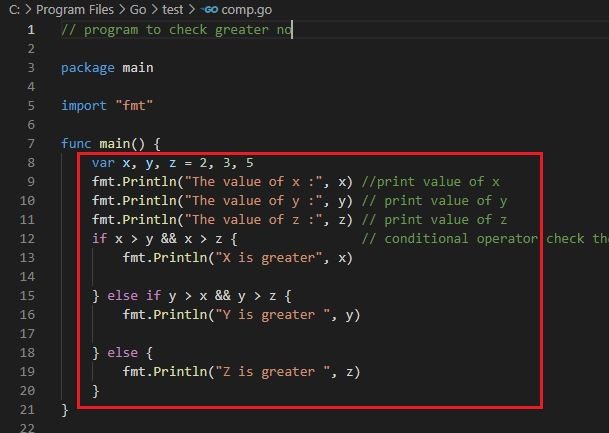
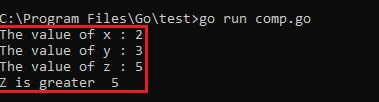
Output :
Increment [++] and decrement [- -] operator
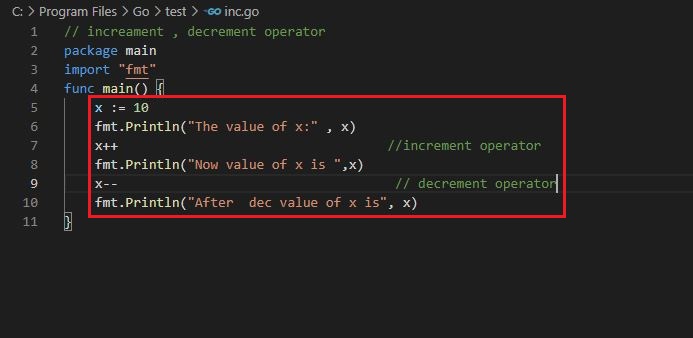
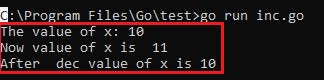
Output :
Logical operators
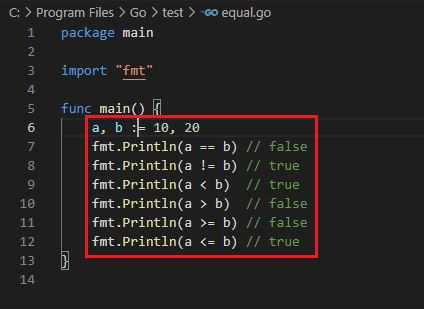
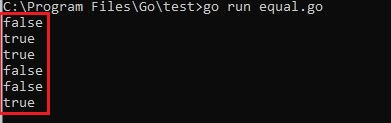
Output :
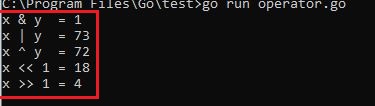
Shift operator
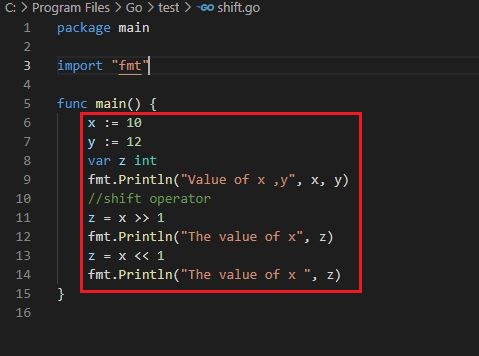
Output :
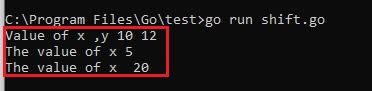
Bitwise Operators
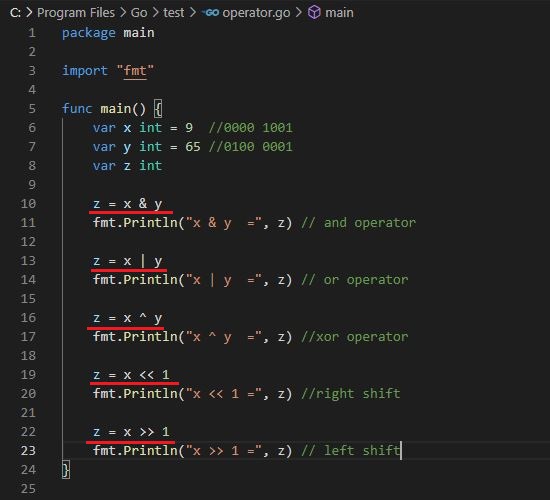
Output :