Go – if-else use cases
The if statement in Go is use to test the condition. If it evaluates to true, the body of the statement is executed. If it evaluates to false, if block is skip.
Syntax :
if(boolean_expression)
{
/* statement(s) got executed only if the expression results in true */
}
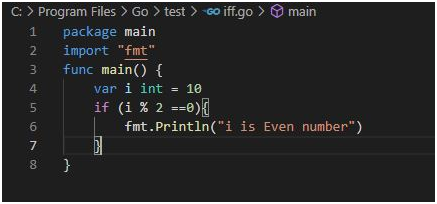
Use Case 1:
package main
import “fmt”
funcmain() {
var a int = 10
if( a % 2==0 ) { // if condition is true then print the following
fmt.Printf(“a is even number” )
}
}
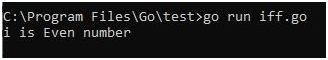
Output:
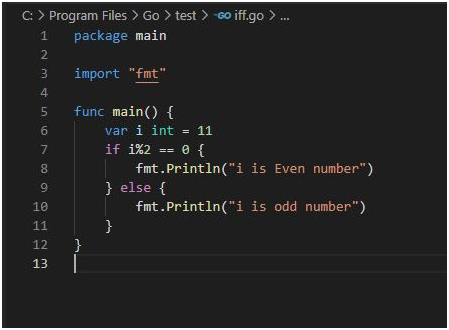
Use Case 2:
package main
import “fmt”
funcmain() {
var iint = 10;
if ( i%2 == 0 ) {
/* if condition is true then print the following */
fmt.Printf(“i is even number”);
} else {
/* if condition is false then print the following */
fmt.Printf(“i is odd number”);
}
}
Output:
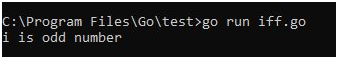
Use Case 3:
package main
import “fmt”
funcmain() {
fmt.Print(“Enter number: “)
var i int
fmt.Scanln(&i)
fmt.Print(i)
/* check the boolean condition */
if( i % 2==0 ) {
fmt.Println(” is even” );
} else {
fmt.Println(” is odd” );
}
}
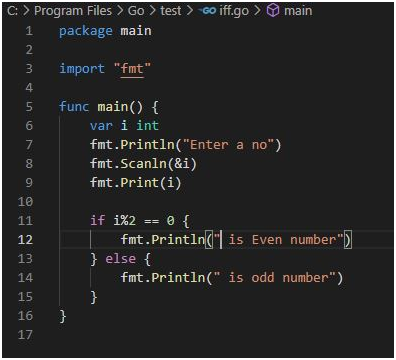
Output:
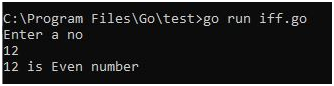
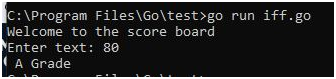
Use Case 4:
package main
import “fmt”
funcmain() {
fmt.Print(“Enter text: “)
var input int
fmt.Scanln(&input)
if (input < 0 || input > 100) {
fmt.Print(“Please enter valid no”)
} else if (input >= 0 && input <50 ) {
fmt.Print(” Fail”)
} else if (input >= 50 && input < 60) {
fmt.Print(” D Grade”)
} else if (input >= 60 && input <70 ) {
fmt.Print(” C Grade”)
} else if (input >= 70 && input < 80) {
fmt.Print(” B Grade”)
} else if (input >= 80 && input <90 ) {
fmt.Print(” A Grade”)
} else if (input >= 90 && input <= 100) {
fmt.Print(” A+ Grade”)
}
}
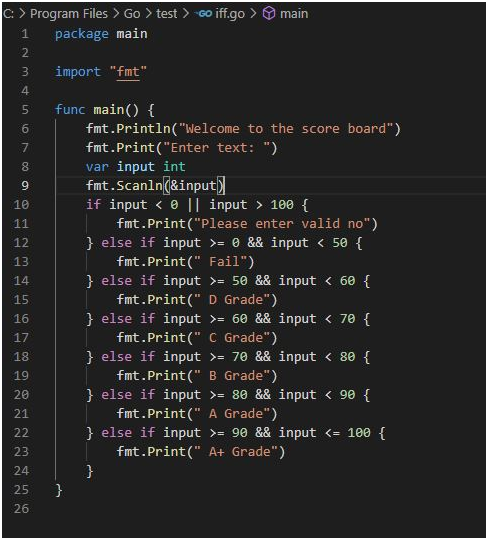
Output: