Decision Tree Introduction with Examples
Decision Tree Introduction with examples, Are you the one who is looking forward to knowing Decision tree Introduction with Examples? Or the one who is looking forward to knowing types of decision tree algorithm in Machine Learning and How to create Decision Tree or Are you dreaming to become to certified Pro Machine Learning Engineer or Data Scientist, then stop just dreaming, get your Data Science certification course with Machine Learning from India’s Leading Data Science training institute.
A Decision tree has analogies in real life and influenced both classification and regression in Machine Learning. A decision tree represents decisions and decision making visually. In this blog, we will learn types of Decision tree Introduction, types of decision tree algorithm, How to create Decision Trees, Advantages, and Disadvantages of Decision Tree. Do you want to know Steps for Decision tree using Python in machine learning, So follow the below-mentioned Decision tree Introduction with examples in Machine Learning from Prwatech and take advanced Data Science training like a pro from today itself under 10+ Years of hands-on experienced Professionals.
Decision Tree in Machine Learning
The decision tree stands out as the most influential and popular tool for classification and prediction. In essence, a decision tree forms a structured representation wherein each interior node represents a test on a feature. Subsequently, each leaf node signifies a class label, while branches denote combinations of features that contribute to those class labels. Notably, the paths extending from the root to the leaf provide discernible classification rules.
The decision tree algorithm falls under the type of supervised learning. It can be applied in cases of both regression and classification problems. A tree representation is used by a Decision tree to solve a problem where every leaf node resembles a class label and attributes represent the internal node of a tree.
Common terms used with Decision trees:
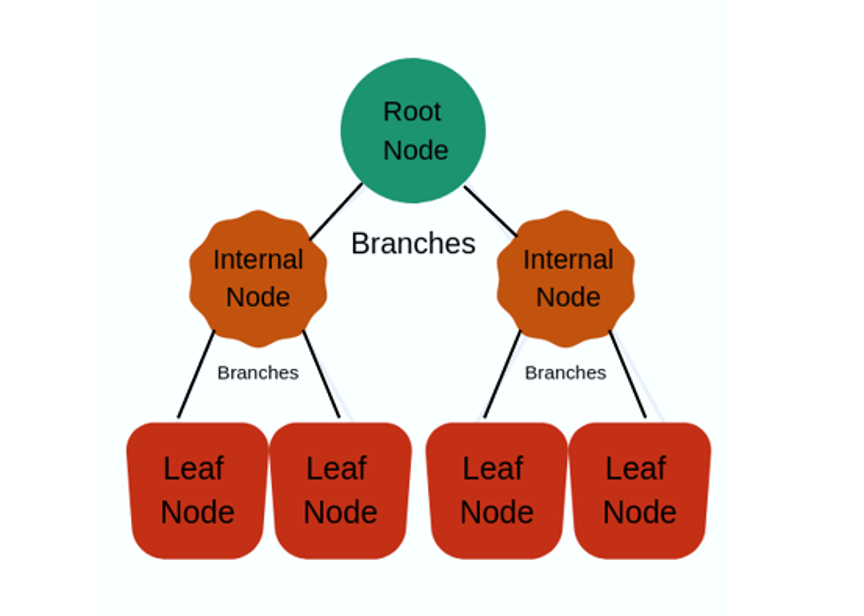
How to create a Decision Tree
While creating a decision tree, on every node of a tree we have to ask a different types of questions. Based on the asked question we will calculate the information gain corresponding to it.
Entropy:
Entropy is a measure of uncertainty of a random variable. It symbolizes the impurity of a random collection of examples. The greater entropy indicates higher information content.
Information Gain:
It is the entity that is required to decide which feature is to split or divide it on at every step in building the tree. To keep tree small, at every step we should select the split that outcomes in the purest child nodes. Information is a commonly used measure of purity.
Information value measures the quantity of information, a feature giving about the class. The field has the highest information gain will be taken as the main field to split the whole dataset. This process will continue until all children nodes are pure, or until the information gain is 0.
Usually, decision tree creation works top-down. It selects a variable at each step that best splits the set of items. Different algorithms follow different matrices for measuring best. Suppose X is a set of instances, P is an attribute, Xv is the subset of X with P = v, and Values (P) is the set of all possible values of P, then
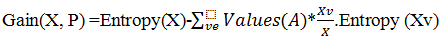
Information Gain Example:
For the set X = {a,a,b,b,b,b,a,b,a,b}
Total instances = 10
The occurrence of ‘a’ = 4
The occurrence of ‘b’ = 6
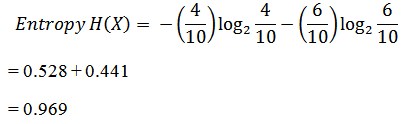
Gini Impurity
It is a calculation of the probability of an inaccurate classification of a new instance for a random variable if the new instance is randomly classified according to the distribution of class labels from the data set. If the dataset is pure then the probability of incorrect classification is 0. If the input sample is a mixture of a variety of classes then the likelihood of inaccurate classification will be high.
Decision Tree Algorithm Example:
Let’s take a weather report into consideration for classifying on basis of different categories. The target here is to decide whether to play cricket or not for a particular day.
| Day | Weather | Temperature | Humidity | Wind |
| 1 | Sunny | Hot | High | Weak |
| 2 | Cloudy | Hot | High | Weak |
| 3 | Sunny | Mild | Normal | Strong |
| 4 | Cloudy | Mild | High | Strong |
| 5 | Rainy | Mild | High | Strong |
| 6 | Rainy | Cool | Normal | Strong |
| 7 | Rainy | Mild | High | Weak |
Now based on the Decision tree hierarchy, first we have to find here, which feature is the root node. Here we have to calculate ‘Entropy’ for that feature. It can be calculated as:
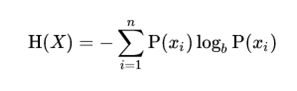
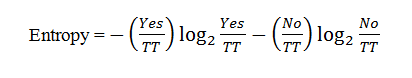
Where TT= Total number of targets=14
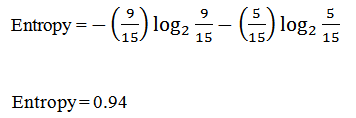
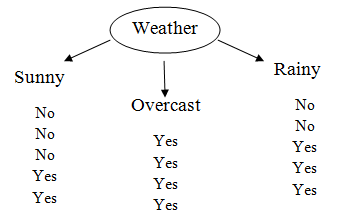
First, we check for the feature ‘Weather’. This image shows the distribution of the target variable depending on subcategories. It is having three subcategories as ‘Sunny’, ‘Overcast’, and ‘Rainy’. We will first calculate individual entropy for each subcategory. It is giving target value yes or No as follows:
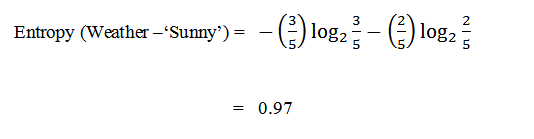
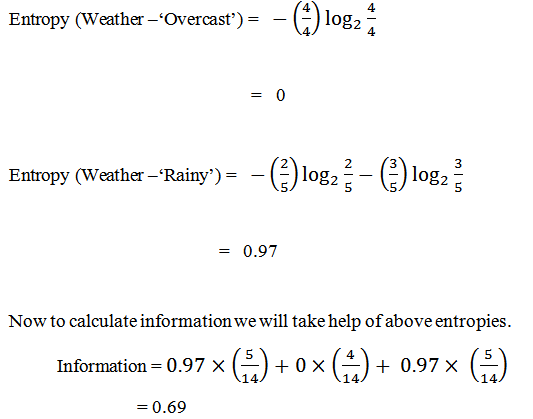
It is information for ‘Weather’. To check the information gain we have to subtract information from total entropy.
Information gain = Entropy – information
= 0.94 – 0.69
= 0.25
Like this, if we calculate the information gain for all features we get:
Gain for temperature = 0.03
Information Gain of Humidity = 0.152
Wind = 0.048
It is clearly observed that from the calculation, the information gain of Weather is highest among all. So ‘Weather’ will be the root node. After this, the table is modified by excluding the column of Weather. And the procedure is repeated to get the next internal or leaf nodes. Those whose information gain is very negligible are eliminated. Finally, we get a structure of a decision tree like this:
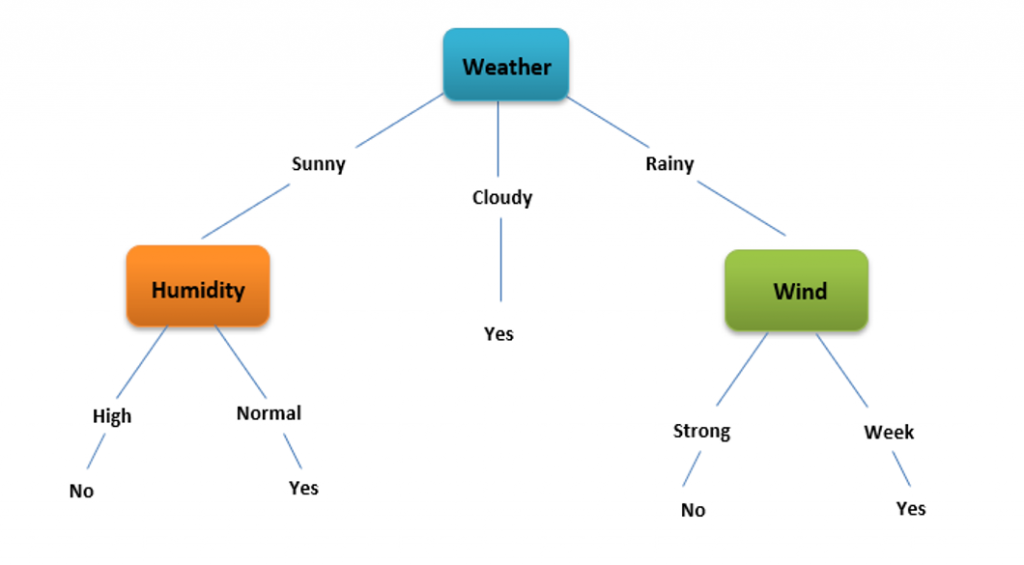
Types of Decision Tree Algorithm
Decision trees are created algorithmically by determining ways to split a dataset based on different conditions. They represent one of the most commonly used and practical methods for supervised learning, being non-parametric and applicable to both classification and regression tasks.
In classification trees, the target variable assumes a discrete set of values, while regression trees deal with target variables having continuous values, often referred to as CART (Classification and Regression Tree).
Advantages of Decision Tree
Decision trees offer several advantages:
- Easy implementation and understanding.
- Capability to handle both classification and regression data.
- Resistance to outliers, although some data pre-processing may be necessary.
Disadvantages of Decision Tree
However, there are some drawbacks:
- Susceptibility to overfitting.
- Requirement for performance measurement.
- Necessity for proper parameter tuning.
To address overfitting in decision tree models, pruning is commonly employed. Pruning involves the removal of branches utilizing features with low significance, thereby reducing the tree’s complexity. This reduction mitigates overfitting, leading to improved generalization on new test samples.
Pruning aims to decrease the decision tree’s size while preserving predictive accuracy, typically evaluated using a cross-validation set. There are two major pruning techniques:
- Minimum Error: This approach trims the tree to minimize cross-validated error.
- Smallest Tree: Here, the tree is pruned slightly beyond the point of minimum error to ensure the cross-validation error remains within 1 standard error of the minimum error.
Steps for Decision tree using Python
Import Library
from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Import the data set.
data = pd.read_csv(“Your File Path”)
Divide the data set into independent and dependent parts.
X = data.iloc[:,0:20] #independent columns
y = data.iloc[:,-1] #dependent columns
Perform feature selection. Perform Label Encoding if the data set contains any string values. Check whether the data set contains any null values or not.
data.isna().any()
Perform different Data Cleaning operations to remove null values.
Split the data set into two parts for training and testing.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, random_state = 47, test_size = 0.33)
Import Decision Tree from sklearn
from sklearn. tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
Create tree object and train the model using the training sets and check score
model = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion=’gini’)
# Here we can change the algorithm as gini or entropy by default it is gini for classification.
model = tree.DecisionTreeRegressor() for regression
model.fit(X, y)
model.score(X, y)
Predict Output and calculate the accuracy percentage of the model created.
predicted = model.predict(x_test)
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
print(‘Accuracy Score on train data: ‘, accuracy_score(y_true=y_train, y_pred=clf.predict(X_train))*100)
print(‘Accuracy Score on test data: ‘, accuracy_score(y_true=y_test, y_pred=y_pred)*100).
We hope you understand the Decision tree Introduction with examples in Machine Learning concepts and types of decision tree algorithm, Advantages of Decision Tree, Disadvantages of Decision Tree, and Steps for Decision tree using Python. Get success in your career as a Data Scientist/ Machine Learning Engineer by being a part of the Prwatech, India’s leading Data Science training institute in Bangalore.


